K230 nncase Development Guide#

Copyright © 2023 Beijing Canaan Creative Information Technology Co., Ltd.
Disclaimer#
The products, services, or features you purchase are subject to the commercial contracts and terms of Beijing Canaan Creative Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“the Company” hereinafter) and its affiliates. All or part of the products, services, or features described in this document may not be within the scope of your purchase or use. Unless otherwise agreed in the contract, the Company does not provide any express or implied statements or warranties regarding the correctness, reliability, completeness, merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, and non-infringement of any representations, information, or content in this document. Unless otherwise agreed, this document is for reference only.
Due to product version upgrades or other reasons, the content of this document may be updated or modified periodically without any notice.
Trademark Statement#
 , “Canaan,” and other Canaan trademarks are trademarks of Beijing Canaan Creative Information Technology Co., Ltd. and its affiliates. All other trademarks or registered trademarks mentioned in this document are owned by their respective owners.
, “Canaan,” and other Canaan trademarks are trademarks of Beijing Canaan Creative Information Technology Co., Ltd. and its affiliates. All other trademarks or registered trademarks mentioned in this document are owned by their respective owners.
Copyright © 2023 Beijing Canaan Creative Information Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Without the written permission of the Company, no unit or individual may excerpt, copy part or all of the content of this document, or disseminate it in any form.
Table of Contents#
[TOC]
Preface#
Overview#
This document is the user guide for K230 nncase, providing users with instructions on how to install nncase, how to call compiler APIs to compile neural network models, and how to write AI inference programs using runtime APIs.
Target Audience#
This document (this guide) is mainly intended for the following personnel:
Technical support engineers
Software development engineers
Abbreviation Definitions#
Abbreviation |
Description |
|---|---|
PTQ |
Post-training quantization |
MSE |
Mean-square error |
Revision History#
Document Version |
Modification Description |
Modifier |
Date |
|---|---|---|---|
V1.0 |
Initial version |
Zhang Yang/Huo Chenghai |
2023/4/7 |
V1.1 |
Unified to Word format, improved ai2d |
Zhang Yang/Huo Chenghai |
2023/5/5 |
V1.2 |
New architecture for nncase v2 |
Zhang Yang/Zheng Qihang/Huo Chenghai |
2023/6/2 |
V1.3 |
nncase_k230_v2.1.0, ai2d/runtime_tensor supports physical address |
Zhang Yang |
2023/7/3 |
V1.4 |
Document description updated |
Yang Haoqi |
2024/5/15 |
1. Overview#
1.1 What is nncase#
nncase is a neural network compiler designed for AI accelerators. Currently supported targets include CPU/K210/K510/K230, etc.
Features provided by nncase:
Supports multi-input multi-output networks and multi-branch structures
Static memory allocation, no heap memory required
Operator fusion and optimization
Supports float and uint8/int8 quantized inference
Supports post-training quantization using floating-point models and quantization calibration sets
Flat model, supports zero-copy loading
Supported neural network model formats by nncase:
TFLite
ONNX
1.2 nncase Architecture#
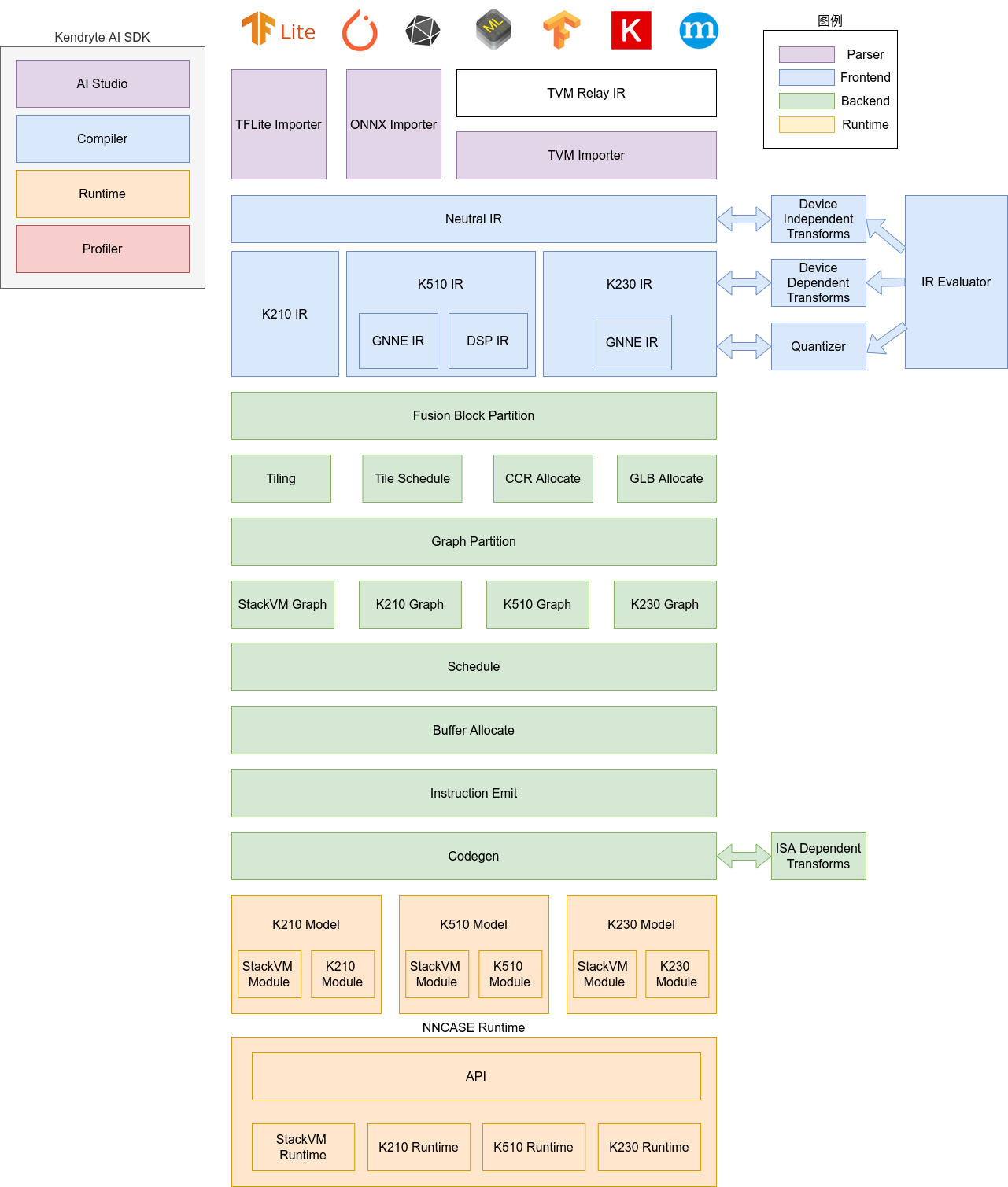
The nncase software stack includes two parts: compiler and runtime.
Compiler: Used to compile neural network models on a PC, ultimately generating kmodel files. It mainly includes modules such as importer, IR, Evaluator, Quantize, Transform optimization, Tiling, Partition, Schedule, and Codegen.
Importer: Imports models from other neural network frameworks into nncase
IR: Intermediate Representation, divided into Neutral IR (device-independent) imported by the importer and Target IR (device-specific) generated by lowering the Neutral IR
Evaluator: Provides interpretation execution capabilities for IR, often used in scenarios such as Constant Folding/PTQ Calibration
Transform: Used for IR transformation and graph traversal optimization
Quantize: Post-training quantization, adds quantization tags to the tensors to be quantized, collects tensor data ranges by calling the Evaluator for interpretation execution based on the input calibration set, inserts quantization/dequantization nodes, and finally optimizes to eliminate unnecessary quantization/dequantization nodes
Tiling: Due to the limited memory capacity of NPU, large computations need to be split. Additionally, choosing Tiling parameters when there is a large amount of data reuse in computations can impact latency and bandwidth
Partition: Splits the graph according to ModuleType, each subgraph corresponds to a RuntimeModule, and different types of RuntimeModules correspond to different Devices (CPU/K230)
Schedule: Generates the computation order and allocates buffers based on the data dependency relationships in the optimized graph
Codegen: Calls the codegen corresponding to each subgraph’s ModuleType to generate RuntimeModules
Runtime: Integrated into the user’s App, providing functions such as loading kmodel, setting input data, executing KPU, and retrieving output data.
1.3 Development Environment#
1.3.1 Operating System#
Supported operating systems include Ubuntu 18.04/Ubuntu 20.04
1.3.2 Software Environment#
No. |
Software |
Version |
|---|---|---|
1 |
python |
3.6/3.7/3.8/3.9/3.10 |
2 |
pip |
>=20.3 |
3 |
numpy |
1.19.5 |
4 |
onnx |
1.9.0 |
5 |
onnx-simplifier |
0.3.6 |
6 |
Onnxoptimizer |
0.2.6 |
7 |
Onnxruntime |
1.8.0 |
8 |
dotnet-runtime |
7.0 |
1.3.3 Hardware Environment#
K230 evb
2. Model Compilation APIs (Python)#
nncase provides Python APIs for compiling neural network models on a PC
2.1 Supported Operators#
2.1.1 TFLite Operators#
Operator |
Is Supported |
|---|---|
ABS |
Yes |
ADD |
Yes |
ARG_MAX |
Yes |
ARG_MIN |
Yes |
AVERAGE_POOL_2D |
Yes |
BATCH_MATMUL |
Yes |
CAST |
Yes |
CEIL |
Yes |
CONCATENATION |
Yes |
CONV_2D |
Yes |
COS |
Yes |
CUSTOM |
Yes |
DEPTHWISE_CONV_2D |
Yes |
DIV |
Yes |
EQUAL |
Yes |
EXP |
Yes |
EXPAND_DIMS |
Yes |
FLOOR |
Yes |
FLOOR_DIV |
Yes |
FLOOR_MOD |
Yes |
FULLY_CONNECTED |
Yes |
GREATER |
Yes |
GREATER_EQUAL |
Yes |
L2_NORMALIZATION |
Yes |
LEAKY_RELU |
Yes |
LESS |
Yes |
LESS_EQUAL |
Yes |
LOG |
Yes |
LOGISTIC |
Yes |
MAX_POOL_2D |
Yes |
MAXIMUM |
Yes |
MEAN |
Yes |
MINIMUM |
Yes |
MUL |
Yes |
NEG |
Yes |
NOT_EQUAL |
Yes |
PAD |
Yes |
PADV2 |
Yes |
MIRROR_PAD |
Yes |
PACK |
Yes |
POW |
Yes |
REDUCE_MAX |
Yes |
REDUCE_MIN |
Yes |
REDUCE_PROD |
Yes |
RELU |
Yes |
PRELU |
Yes |
RELU6 |
Yes |
RESHAPE |
Yes |
RESIZE_BILINEAR |
Yes |
RESIZE_NEAREST_NEIGHBOR |
Yes |
ROUND |
Yes |
RSQRT |
Yes |
SHAPE |
Yes |
SIN |
Yes |
SLICE |
Yes |
SOFTMAX |
Yes |
SPACE_TO_BATCH_ND |
Yes |
SQUEEZE |
Yes |
BATCH_TO_SPACE_ND |
Yes |
STRIDED_SLICE |
Yes |
SQRT |
Yes |
SQUARE |
Yes |
SUB |
Yes |
SUM |
Yes |
TANH |
Yes |
TILE |
Yes |
TRANSPOSE |
Yes |
TRANSPOSE_CONV |
Yes |
QUANTIZE |
Yes |
FAKE_QUANT |
Yes |
DEQUANTIZE |
Yes |
GATHER |
Yes |
GATHER_ND |
Yes |
ONE_HOT |
Yes |
SQUARED_DIFFERENCE |
Yes |
LOG_SOFTMAX |
Yes |
SPLIT |
Yes |
HARD_SWISH |
Yes |
2.1.2 ONNX Operators#
Operator |
Is Supported |
|---|---|
Abs |
Yes |
Acos |
Yes |
Acosh |
Yes |
And |
Yes |
ArgMax |
Yes |
ArgMin |
Yes |
Asin |
Yes |
Asinh |
Yes |
Add |
Yes |
AveragePool |
Yes |
BatchNormalization |
Yes |
Cast |
Yes |
Ceil |
Yes |
Celu |
Yes |
Clip |
Yes |
Compress |
Yes |
Concat |
Yes |
Constant |
Yes |
ConstantOfShape |
Yes |
Conv |
Yes |
ConvTranspose |
Yes |
Cos |
Yes |
Cosh |
Yes |
CumSum |
Yes |
DepthToSpace |
Yes |
DequantizeLinear |
Yes |
Div |
Yes |
Dropout |
Yes |
Elu |
Yes |
Exp |
Yes |
Expand |
Yes |
Equal |
Yes |
Erf |
Yes |
Flatten |
Yes |
Floor |
Yes |
Gather |
Yes |
GatherElements |
Yes |
GatherND |
Yes |
Gemm |
Yes |
GlobalAveragePool |
Yes |
GlobalMaxPool |
Yes |
Greater |
Yes |
GreaterOrEqual |
Yes |
GRU |
Yes |
Hardmax |
Yes |
HardSigmoid |
Yes |
HardSwish |
Yes |
Identity |
Yes |
InstanceNormalization |
Yes |
LayerNormalization |
Yes |
LpNormalization |
Yes |
LeakyRelu |
Yes |
Less |
Yes |
LessOrEqual |
Yes |
Log |
Yes |
LogSoftmax |
Yes |
LRN |
Yes |
LSTM |
Yes |
MatMul |
Yes |
MaxPool |
Yes |
Max |
Yes |
Min |
Yes |
Mul |
Yes |
Neg |
Yes |
Not |
Yes |
OneHot |
Yes |
Pad |
Yes |
Pow |
Yes |
PRelu |
Yes |
QuantizeLinear |
Yes |
RandomNormal |
Yes |
RandomNormalLike |
Yes |
RandomUniform |
Yes |
RandomUniformLike |
Yes |
ReduceL1 |
Yes |
ReduceL2 |
Yes |
ReduceLogSum |
Yes |
ReduceLogSumExp |
Yes |
ReduceMax |
Yes |
ReduceMean |
Yes |
ReduceMin |
Yes |
ReduceProd |
Yes |
ReduceSum |
Yes |
ReduceSumSquare |
Yes |
Relu |
Yes |
Reshape |
Yes |
Resize |
Yes |
ReverseSequence |
Yes |
RoiAlign |
Yes |
Round |
Yes |
Rsqrt |
Yes |
Selu |
Yes |
Shape |
Yes |
Sign |
Yes |
Sin |
Yes |
Sinh |
Yes |
Sigmoid |
Yes |
Size |
Yes |
Slice |
Yes |
Softmax |
Yes |
Softplus |
Yes |
Softsign |
Yes |
SpaceToDepth |
Yes |
Split |
Yes |
Sqrt |
Yes |
Squeeze |
Yes |
Sub |
Yes |
Sum |
Yes |
Tanh |
Yes |
Tile |
Yes |
TopK |
Yes |
Transpose |
Yes |
Trilu |
Yes |
ThresholdedRelu |
Yes |
Upsample |
Yes |
Unsqueeze |
Yes |
Where |
Yes |
2.2 APIs#
Currently, the model compilation APIs support deep learning models in TFLite/ONNX formats.
2.2.1 CompileOptions#
Description:
The CompileOptions class is used to configure nncase compilation options. The descriptions of each attribute are as follows:
Attribute Name |
Type |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
target |
string |
Yes |
Specifies the compilation target, such as ‘cpu’ or ‘k230’ |
dump_ir |
bool |
No |
Specifies whether to dump IR, defaults to False |
dump_asm |
bool |
No |
Specifies whether to dump asm assembly files, defaults to False |
dump_dir |
string |
No |
Specifies the directory to dump files when dump_ir or other dump options are enabled, defaults to “” |
input_file |
string |
No |
Specifies the parameter file path when the ONNX model exceeds 2GB, defaults to “” |
preprocess |
bool |
No |
Specifies whether to enable preprocessing, defaults to False. The following parameters are effective only when |
input_type |
string |
No |
Specifies the input data type when preprocessing is enabled, defaults to “float”. When |
input_shape |
list[int] |
No |
Specifies the shape of the input data when preprocessing is enabled, defaults to []. When |
input_range |
list[float] |
No |
Specifies the floating-point range of the input data after dequantization when preprocessing is enabled, defaults to []. When |
input_layout |
string |
No |
Specifies the layout of the input data, defaults to “” |
swapRB |
bool |
No |
Specifies whether to reverse the data in the |
mean |
list[float] |
No |
Mean value for preprocessing normalization, defaults to [0,0,0] |
std |
list[float] |
No |
Standard deviation for preprocessing normalization, defaults to [1,1,1] |
letterbox_value |
float |
No |
Specifies the fill value for letterbox preprocessing, defaults to 0 |
output_layout |
string |
No |
Specifies the layout of the output data, defaults to “” |
shape_bucket_enable |
bool |
Yes |
Specifies whether to enable ShapeBucket functionality, defaults to False. Effective when |
shape_bucket_range_info |
Dict[str, [int, int]] |
Yes |
Specifies the range of variables in each dimension of the input shape, minimum value must be greater than or equal to 1 |
shape_bucket_segments_count |
int |
Yes |
Specifies the number of segments to divide the input variable’s range |
shape_bucket_fix_var_map |
Dict[str, int] |
No |
Specifies fixed values for variables in the shape dimension information |
2.2.1.1 Preprocessing Workflow#
Currently, custom preprocessing order is not supported. You can configure the required preprocessing parameters based on the following workflow diagram.
(shape = input_shape
dtype = input_type)") -->a(input_layout != ' ')-.Y.->Transpose1["transpose"] -.->b("SwapRB == True")-.Y.->SwapRB["SwapRB"]-.->c("input_type != float32")-.Y.->Dequantize["Dequantize"]-.->d("input_HW != model_HW")-.Y.->LetterBox["LetterBox"] -.->e("std not empty
mean not empty")-.Y.->Normalization["Normalization"]-.->OldInput-->Model_body-->OldOutput-->f("output_layout != ' '")-.Y.->Transpose2["Transpose"]-.-> NewOutput; a--N-->b--N-->c--N-->d--N-->e--N-->OldInput; f--N-->NewOutput; subgraph origin_model OldInput; Model_body ; OldOutput; end
Parameter explanations:
input_rangespecifies the floating-point range after dequantization when the input data type is fixed-point.a. If the input data type is uint8 and the range is [0,255], setting
input_rangeto [0,255] means dequantization only converts the data type from uint8 to float32. Themeanandstdparameters should still be specified based on data in the range [0,255].b. If the input data type is uint8 and the range is [0,255], setting
input_rangeto [0,1] means dequantization will convert fixed-point data to floating-point data in the range [0,1]. Themeanandstdparameters should be specified based on data in the range [0,1].graph TD; NewInput_uint8("NewInput_uint8
[input_type:uint8]") --input_range:0,255 -->dequantize_0["Dequantize"]--float range:0,255--> OldInput_float32 NewInput_uint81("NewInput_uint8
[input_type:uint8]") --input_range:0,1 -->dequantize_1["Dequantize"]--float range:0,1--> OldInput_float32input_shapespecifies the shape of the input data, andinput_layoutspecifies its layout. It currently supports both string (e.g.,"NHWC","NCHW") and index formats. Non-4D data processing is also supported. When configured as a string,input_layoutspecifies the layout of the input data. When configured as an index,input_layoutspecifies the permutation parameter for aTransposeoperation.
Similarly, output_layout can be configured as shown below.
NHWC"); OldOutput("OldOutput: (NCHW)") --"output_layout: "0,2,3,1""--> Transpose4("Transpose perm: 0,2,3,1") --> NewOutput("NewOutput
NHWC"); end
2.2.1.2 Dynamic Shape Parameters#
ShapeBucket is a solution for dynamic shapes that optimizes based on the range of input lengths and the specified number of segments. This feature is disabled by default and needs to be enabled through the corresponding option. Apart from specifying the relevant field information, the rest of the compilation process is the same as compiling a static model.
ONNX
In the shape information of a model, some dimensions may be variable names. For example, consider an ONNX model with the following inputs:
tokens: int64[batch_size, tgt_seq_len]
step: float32[seq_len, batch_size]
The shape information contains three variables: seq_len, tgt_seq_len, and batch_size. Although batch_size is a variable, it is fixed to 3 in actual use. Therefore, add batch_size = 3 to fix_var_map to fix this dimension to 3 during runtime. The variables seq_len and tgt_seq_len are dynamic and need to be configured with their actual ranges in range_info. segments_count specifies the number of segments to divide the range into, which will proportionally increase the compilation time.
Here is an example of the corresponding compilation parameters:
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.shape_bucket_enable = True
compile_options.shape_bucket_range_info = {"seq_len": [1, 100], "tgt_seq_len": [1, 100]}
compile_options.shape_bucket_segments_count = 2
compile_options.shape_bucket_fix_var_map = {"batch_size": 3}
TFLite
Unlike ONNX models, TFLite models do not currently label dimension names in the shape. Currently, only one dimension in the input can be dynamic, and it is uniformly named as -1. The configuration is as follows:
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.shape_bucket_enable = True
compile_options.shape_bucket_range_info = {"-1":[1, 100]}
compile_options.shape_bucket_segments_count = 2
compile_options.shape_bucket_fix_var_map = {"batch_size" : 3}
After configuring these options, the entire compilation process is the same as for a static shape model.
2.2.1.3 Parameter Configuration Example#
Instantiate CompileOptions and configure the attribute values.
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = "cpu" # "k230"
compile_options.dump_ir = True # if False, will not dump the compile-time result.
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = "dump_path"
compile_options.input_file = ""
# preprocess args
compile_options.preprocess = False
if compile_options.preprocess:
compile_options.input_type = "uint8" # "uint8" "float32"
compile_options.input_shape = [1,224,320,3]
compile_options.input_range = [0,1]
compile_options.input_layout = "NHWC" # "NHWC" "NCHW"
compile_options.swapRB = False
compile_options.mean = [0,0,0]
compile_options.std = [1,1,1]
compile_options.letterbox_value = 0
compile_options.output_layout = "NHWC" # "NHWC" "NCHW"
# Dynamic shape args
compile_options.shape_bucket_enable = False
if compile_options.shape_bucket_enable:
compile_options.shape_bucket_range_info = {"seq_len": [1, 100], "tgt_seq_len": [1, 100]}
compile_options.shape_bucket_segments_count = 2
compile_options.shape_bucket_fix_var_map = {"batch_size": 3}
2.2.2 ImportOptions#
Description:
The ImportOptions class is used to configure nncase import options.
Definition:
class ImportOptions:
def __init__(self) -> None:
pass
Example:
Instantiate ImportOptions and configure attribute values.
#import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
2.2.3 PTQTensorOptions#
Description:
The PTQTensorOptions class is used to configure nncase PTQ options.
Name |
Type |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
samples_count |
int |
No |
Specifies the number of samples used for the quantization calibration set |
calibrate_method |
string |
No |
Specifies the quantization method, options are ‘NoClip’ and ‘Kld’, default is ‘Kld’ |
finetune_weights_method |
string |
No |
Specifies whether to fine-tune weights, options are ‘NoFineTuneWeights’ and ‘UseSquant’, default is ‘NoFineTuneWeights’ |
quant_type |
string |
No |
Specifies the data quantization type, options are ‘uint8’, ‘int8’, ‘int16’ |
w_quant_type |
string |
No |
Specifies the weight quantization type, options are ‘uint8’, ‘int8’, ‘int16’ |
No |
The above two types cannot both be ‘int16’ |
||
quant_scheme |
string |
No |
Path to the quantization parameter configuration file |
quant_scheme_strict_mode |
bool |
No |
Whether to strictly follow quant_scheme for quantization |
export_quant_scheme |
bool |
No |
Whether to export the quantization parameter configuration file |
export_weight_range_by_channel |
bool |
No |
Whether to export weights quantization parameters in |
For detailed usage of mixed quantization, see MixQuant Guide
Example:
# ptq_options
ptq_options = nncase.PTQTensorOptions()
ptq_options.samples_count = 6
ptq_options.finetune_weights_method = "NoFineTuneWeights"
ptq_options.quant_type = "uint8"
ptq_options.w_quant_type = "uint8"
ptq_options.set_tensor_data(generate_data(input_shape, ptq_options.samples_count, args.dataset))
ptq_options.quant_scheme = ""
ptq_options.quant_scheme_strict_mode = False
ptq_options.export_quant_scheme = True
ptq_options.export_weight_range_by_channel = True
compiler.use_ptq(ptq_options)
2.2.4 set_tensor_data#
Description:
Sets tensor data.
Definition:
def set_tensor_data(self, data: List[List[np.ndarray]]) -> None:
reshape_data = list(map(list, zip(*data)))
self.cali_data = [RuntimeTensor.from_numpy(
d) for d in itertools.chain.from_iterable(reshape_data)]
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
data |
List[List[np.ndarray]] |
Calibration data |
[Return Value]
None
Example:
# ptq_options
ptq_options = nncase.PTQTensorOptions()
ptq_options.samples_count = 6
ptq_options.set_tensor_data(generate_data(input_shape, ptq_options.samples_count, args.dataset))
compiler.use_ptq(ptq_options)
2.2.5 Compiler#
Description:
The Compiler class is used to compile neural network models.
Definition:
class Compiler:
_target: _nncase.Target
_session: _nncase.CompileSession
_compiler: _nncase.Compiler
_compile_options: _nncase.CompileOptions
_quantize_options: _nncase.QuantizeOptions
_module: IRModule
2.2.6 import_tflite#
Description:
Imports a TFLite model.
Definition:
def import_tflite(self, model_content: bytes, options: ImportOptions) -> None:
self._compile_options.input_format = "tflite"
self._import_module(model_content)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
model_content |
byte[] |
The content of the model |
import_options |
ImportOptions |
Import options |
[Return Value]
None
Example:
model_content = read_model_file(model)
compiler.import_tflite(model_content, import_options)
2.2.7 import_onnx#
Description:
Imports an ONNX model.
Definition:
def import_onnx(self, model_content: bytes, options: ImportOptions) -> None:
self._compile_options.input_format = "onnx"
self._import_module(model_content)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
model_content |
byte[] |
The content of the model |
import_options |
ImportOptions |
Import options |
[Return Value]
None
Example:
model_content = read_model_file(model)
compiler.import_onnx(model_content, import_options)
2.2.8 use_ptq#
Description:
Sets PTQ configuration options.
Quantization is mandatory for K230 by default.
Definition:
use_ptq(ptq_options)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ptq_options |
PTQTensorOptions |
PTQ configuration options |
[Return Value]
None
Example:
compiler.use_ptq(ptq_options)
2.2.9 compile#
Description:
Compiles the neural network model.
Definition:
compile()
[Parameters]
None
[Return Value]
None
Example:
compiler.compile()
2.2.10 gencode_tobytes#
Description:
Generates kmodel byte stream.
Definition:
gencode_tobytes()
[Parameters]
None
[Return Value]
bytes[]
Example:
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(infer_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
2.3 Examples#
The following examples use models and Python compilation scripts.
The original model files are located in
/path/to/k230_sdk/src/big/nncase/examples/modelsThe Python compilation scripts are located in
/path/to/k230_sdk/src/big/nncase/examples/scripts
2.3.1 Compiling a TFLite Model#
The mbv2_tflite.py script is as follows:
import os
import argparse
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import nncase
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def generate_data(shape, batch, calib_dir):
img_paths = [os.path.join(calib_dir, p) for p in os.listdir(calib_dir)]
data = []
for i in range(batch):
assert i < len(img_paths), "calibration images not enough."
img_data = Image.open(img_paths[i]).convert('RGB')
img_data = img_data.resize((shape[3], shape[2]), Image.BILINEAR)
img_data = np.asarray(img_data, dtype=np.uint8)
img_data = np.transpose(img_data, (2, 0, 1))
data.append([img_data[np.newaxis, ...]])
return data
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='model file')
parser.add_argument("--dataset", type=str, help='calibration_dataset')
args = parser.parse_args()
input_shape = [1, 3, 224, 224]
dump_dir = 'tmp/mbv2_tflite'
# compile_options
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.preprocess = True
compile_options.swapRB = False
compile_options.input_shape = input_shape
compile_options.input_type = 'uint8'
compile_options.input_range = [0, 255]
compile_options.mean = [127.5, 127.5, 127.5]
compile_options.std = [127.5, 127.5, 127.5]
compile_options.input_layout = 'NCHW'
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import
model_content = read_model_file(args.model)
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
compiler.import_tflite(model_content, import_options)
# ptq_options
ptq_options = nncase.PTQTensorOptions()
ptq_options.samples_count = 6
ptq_options.set_tensor_data(generate_data(input_shape, ptq_options.samples_count, args.dataset))
compiler.use_ptq(ptq_options)
# compile
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Run the following command to compile the mobilenetv2 TFLite model with the target set to k230:
root@c285a41a7243:/mnt/# cd src/big/nncase/examples
root@c285a41a7243:/mnt/src/big/nncase/examples# python3 ./scripts/mbv2_tflite.py --target k230 --model models/mbv2.tflite --dataset calibration_dataset
2.3.2 Compiling an ONNX Model#
For ONNX models, it is recommended to use the ONNX Simplifier to simplify the model before using nncase to compile it.
The yolov5s_onnx.py script is as follows:
import os
import argparse
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import onnxsim
import onnx
import nncase
def parse_model_input_output(model_file):
onnx_model = onnx.load(model_file)
input_all = [node.name for node in onnx_model.graph.input]
input_initializer = [node.name for node in onnx_model.graph.initializer]
input_names = list(set(input_all) - set(input_initializer))
input_tensors = [
node for node in onnx_model.graph.input if node.name in input_names]
# input
inputs = []
for _, e in enumerate(input_tensors):
onnx_type = e.type.tensor_type
input_dict = {}
input_dict['name'] = e.name
input_dict['dtype'] = onnx.mapping.TENSOR_TYPE_TO_NP_TYPE[onnx_type.elem_type]
input_dict['shape'] = [(i.dim_value if i.dim_value != 0 else d) for i, d in zip(
onnx_type.shape.dim, [1, 3, 224, 224])]
inputs.append(input_dict)
return onnx_model, inputs
def onnx_simplify(model_file, dump_dir):
onnx_model, inputs = parse_model_input_output(model_file)
onnx_model = onnx.shape_inference.infer_shapes(onnx_model)
input_shapes = {}
for input in inputs:
input_shapes[input['name']] = input['shape']
onnx_model, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx_model, input_shapes=input_shapes)
assert check, "Simplified ONNX model could not be validated"
model_file = os.path.join(dump_dir, 'simplified.onnx')
onnx.save_model(onnx_model, model_file)
return model_file
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def generate_data_ramdom(shape, batch):
data = []
for i in range(batch):
data.append([np.random.randint(0, 256, shape).astype(np.uint8)])
return data
def generate_data(shape, batch, calib_dir):
img_paths = [os.path.join(calib_dir, p) for p in os.listdir(calib_dir)]
data = []
for i in range(batch):
assert i < len(img_paths), "calibration images not enough."
img_data = Image.open(img_paths[i]).convert('RGB')
img_data = img_data.resize((shape[3], shape[2]), Image.BILINEAR)
img_data = np.asarray(img_data, dtype=np.uint8)
img_data = np.transpose(img_data, (2, 0, 1))
data.append([img_data[np.newaxis, ...]])
return data
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='model file')
parser.add_argument("--dataset", type=str, help='calibration_dataset')
args = parser.parse_args()
input_shape = [1, 3, 320, 320]
dump_dir = 'tmp/yolov5s_onnx'
if not os.path.exists(dump_dir):
os.makedirs(dump_dir)
# onnx simplify
model_file = onnx_simplify(args.model, dump_dir)
# compile_options
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.preprocess = True
compile_options.swapRB = False
compile_options.input_shape = input_shape
compile_options.input_type = 'uint8'
compile_options.input_range = [0, 255]
compile_options.mean = [0, 0, 0]
compile_options.std = [255, 255, 255]
compile_options.input_layout = 'NCHW'
compile_options.output_layout = 'NCHW'
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import
model_content = read_model_file(model_file)
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
compiler.import_onnx(model_content, import_options)
# ptq_options
ptq_options = nncase.PTQTensorOptions()
ptq_options.samples_count = 6
ptq_options.set_tensor_data(generate_data(input_shape, ptq_options.samples_count, args.dataset))
compiler.use_ptq(ptq_options)
# compile
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Run the following command to compile the ONNX model with the target set to k230:
root@c285a41a7243:/mnt/# cd src/big/nncase/examples
root@c285a41a7243:/mnt/src/big/nncase/examples# python3 ./scripts/yolov5s_onnx.py --target k230 --model models/yolov5s.onnx --dataset calibration_dataset
3. Simulator APIs (Python)#
In addition to model compilation APIs, nncase also provides inference APIs that allow you to run compiled kmodel on a PC to verify if the nncase inference results are consistent with the runtime results of the corresponding deep learning framework.
3.1 APIs#
3.1.1 MemoryRange#
Description:
The MemoryRange class is used to represent a memory range.
Definition:
py::class_<memory_range>(m, "MemoryRange")
.def_readwrite("location", &memory_range::memory_location)
.def_property(
"dtype", [](const memory_range &range) { return to_dtype(range.datatype); },
[](memory_range &range, py::object dtype) { range.datatype = from_dtype(py::dtype::from_args(dtype)); })
.def_readwrite("start", &memory_range::start)
.def_readwrite("size", &memory_range::size);
[Attributes]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
location |
int |
Memory location: 0 for input, 1 for output, 2 for rdata, 3 for data, 4 for shared_data |
dtype |
Python data type |
Data type |
start |
int |
Memory start address |
size |
int |
Memory size |
Example:
mr = nncase.MemoryRange()
3.1.2 RuntimeTensor#
Description:
The RuntimeTensor class is used to represent a runtime tensor.
Definition:
py::class_<runtime_tensor>(m, "RuntimeTensor")
.def_static("from_numpy", [](py::array arr) {
auto src_buffer = arr.request();
auto datatype = from_dtype(arr.dtype());
auto tensor = host_runtime_tensor::create(
datatype,
to_rt_shape(src_buffer.shape),
to_rt_strides(src_buffer.itemsize, src_buffer.strides),
gsl::make_span(reinterpret_cast<gsl::byte *>(src_buffer.ptr), src_buffer.size * src_buffer.itemsize),
[=](gsl::byte *) { arr.dec_ref(); })
.unwrap_or_throw();
arr.inc_ref();
return tensor;
})
.def("copy_to", [](runtime_tensor &from, runtime_tensor &to) {
from.copy_to(to).unwrap_or_throw();
})
.def("to_numpy", [](runtime_tensor &tensor) {
auto host = tensor.as_host().unwrap_or_throw();
auto src_map = std::move(hrt::map(host, hrt::map_read).unwrap_or_throw());
auto src_buffer = src_map.buffer();
return py::array(
to_dtype(tensor.datatype()),
tensor.shape(),
to_py_strides(runtime::get_bytes(tensor.datatype()), tensor.strides()),
src_buffer.data());
})
.def_property_readonly("dtype", [](runtime_tensor &tensor) {
return to_dtype(tensor.datatype());
})
.def_property_readonly("shape", [](runtime_tensor &tensor) {
return to_py_shape(tensor.shape());
});
[Attributes]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
dtype |
Python data type |
Data type of the tensor |
shape |
list |
Shape of the tensor |
3.1.3 from_numpy#
Description:
Constructs a RuntimeTensor object from a numpy.ndarray.
Definition:
from_numpy(py::array arr)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
arr |
numpy.ndarray |
|
[Return Value]
RuntimeTensor
Example:
tensor = nncase.RuntimeTensor.from_numpy(self.inputs[i]['data'])
3.1.4 copy_to#
Description:
Copies a RuntimeTensor.
Definition:
copy_to(RuntimeTensor to)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
to |
RuntimeTensor |
|
[Return Value]
None
Example:
sim.get_output_tensor(i).copy_to(to)
3.1.5 to_numpy#
Description:
Converts a RuntimeTensor to a numpy.ndarray object.
Definition:
to_numpy()
[Parameters]
None
[Return Value]
numpy.ndarray object
Example:
arr = sim.get_output_tensor(i).to_numpy()
3.1.6 Simulator#
Description:
The Simulator class is used to run kmodel inference on a PC.
Definition:
py::class_<interpreter>(m, "Simulator")
.def(py::init())
.def("load_model", [](interpreter &interp, gsl::span<const gsl::byte> buffer) { interp.load_model(buffer).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def_property_readonly("inputs_size", &interpreter::inputs_size)
.def_property_readonly("outputs_size", &interpreter::outputs_size)
.def("get_input_desc", &interpreter::input_desc)
.def("get_output_desc", &interpreter::output_desc)
.def("get_input_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index) { return interp.input_tensor(index).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("set_input_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) { return interp.input_tensor(index, tensor).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("get_output_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index) { return interp.output_tensor(index).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("set_output_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) { return interp.output_tensor(index, tensor).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("run", [](interpreter &interp) { interp.run().unwrap_or_throw(); });
[Attributes]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
inputs_size |
int |
Number of inputs |
outputs_size |
int |
Number of outputs |
Example:
sim = nncase.Simulator()
3.1.7 load_model#
Description:
Loads a kmodel.
Definition:
load_model(model_content)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
model_content |
byte[] |
kmodel byte stream |
[Return Value]
None
Example:
sim.load_model(kmodel)
3.1.8 get_input_desc#
Description:
Gets the description of the input at the specified index.
Definition:
get_input_desc(index)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
index |
int |
Index of the input |
[Return Value]
MemoryRange
Example:
input_desc_0 = sim.get_input_desc(0)
3.1.9 get_output_desc#
Description:
Gets the description of the output at the specified index.
Definition:
get_output_desc(index)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
index |
int |
Index of the output |
[Return Value]
MemoryRange
Example:
output_desc_0 = sim.get_output_desc(0)
3.1.10 get_input_tensor#
Description:
Gets the RuntimeTensor of the input at the specified index.
Definition:
get_input_tensor(index)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
index |
int |
Index of the input tensor |
[Return Value]
RuntimeTensor
Example:
input_tensor_0 = sim.get_input_tensor(0)
3.1.11 set_input_tensor#
Description:
Sets the RuntimeTensor of the input at the specified index.
Definition:
set_input_tensor(index, tensor)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
index |
int |
Index of the input tensor |
tensor |
RuntimeTensor |
Input tensor |
[Return Value]
None
Example:
sim.set_input_tensor(0, nncase.RuntimeTensor.from_numpy(self.inputs[0]['data']))
3.1.12 get_output_tensor#
Description:
Gets the RuntimeTensor of the output at the specified index.
Definition:
get_output_tensor(index)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
index |
int |
Index of the output tensor |
[Return Value]
RuntimeTensor
Example:
output_arr_0 = sim.get_output_tensor(0).to_numpy()
3.1.13 set_output_tensor#
Description:
Sets the RuntimeTensor of the output at the specified index.
Definition:
set_output_tensor(index, tensor)
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
index |
int |
Index of the output tensor |
tensor |
RuntimeTensor |
Output tensor |
[Return Value]
None
Example:
sim.set_output_tensor(0, tensor)
3.1.14 run#
Description:
Runs kmodel inference.
Definition:
run()
[Parameters]
None
[Return Value]
None
Example:
sim.run()
3.2 Examples#
Precondition: The yolov5s_onnx.py script has already compiled the yolov5s.onnx model.
The yolov5s_onnx_simu.py script is located in the /path/to/k230_sdk/src/big/nncase/examples/scripts subdirectory and contains the following content:
import os
import copy
import argparse
import numpy as np
import onnx
import onnxruntime as ort
import nncase
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def cosine(gt, pred):
return (gt @ pred) / (np.linalg.norm(gt, 2) * np.linalg.norm(pred, 2))
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='original model file')
parser.add_argument("--model_input", type=str, help='input bin file for original model')
parser.add_argument("--kmodel", type=str, help='kmodel file')
parser.add_argument("--kmodel_input", type=str, help='input bin file for kmodel')
args = parser.parse_args()
# cpu inference
ort_session = ort.InferenceSession(args.model)
output_names = []
model_outputs = ort_session.get_outputs()
for i in range(len(model_outputs)):
output_names.append(model_outputs[i].name)
model_input = ort_session.get_inputs()[0]
model_input_name = model_input.name
model_input_type = np.float32
model_input_shape = model_input.shape
model_input_data = np.fromfile(args.model_input, model_input_type).reshape(model_input_shape)
cpu_results = []
cpu_results = ort_session.run(output_names, { model_input_name : model_input_data })
# create simulator
sim = nncase.Simulator()
# read kmodel
kmodel = read_model_file(args.kmodel)
# load kmodel
sim.load_model(kmodel)
# read input.bin
# input_tensor=sim.get_input_tensor(0).to_numpy()
dtype = sim.get_input_desc(0).dtype
input = np.fromfile(args.kmodel_input, dtype).reshape([1, 3, 320, 320])
# set input for simulator
sim.set_input_tensor(0, nncase.RuntimeTensor.from_numpy(input))
# simulator inference
nncase_results = []
sim.run()
for i in range(sim.outputs_size):
nncase_result = sim.get_output_tensor(i).to_numpy()
nncase_results.append(copy.deepcopy(nncase_result))
# compare
for i in range(sim.outputs_size):
cos = cosine(np.reshape(nncase_results[i], (-1)), np.reshape(cpu_results[i], (-1)))
print('output {0} cosine similarity : {1}'.format(i, cos))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Run the inference script:
root@5f718e19f8a7:/mnt/# cd src/big/nncase/examples
root@5f718e19f8a7:/mnt/src/big/nncase/examples # export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages/
root@5f718e19f8a7:/mnt/src/big/nncase/examples # python3 scripts/yolov5s_onnx_simu.py --model models/yolov5s.onnx --model_input object_detect/data/input_fp32.bin --kmodel tmp/yolov5s_onnx/test.kmodel --kmodel_input object_detect/data/input_uint8.bin
Comparison of nncase simulator and CPU inference results:
output 0 cosine similarity : 0.9997244477272034
output 1 cosine similarity : 0.999757707118988
output 2 cosine similarity : 0.9997308850288391
4. KPU Runtime APIs (C++)#
4.1 Introduction#
KPU Runtime APIs are used to load kmodel on AI devices, set input data, execute KPU/CPU computation, and get output data, etc.
Currently, only C++ APIs are provided. The relevant header files and static libraries are located in the /path/to/k230_sdk/src/big/nncase/riscv64 directory.
$ tree -L 3 riscv64/
riscv64/
├── gsl
│ └── gsl-lite.hpp
├── nncase
│ ├── include
│ │ └── nncase
│ └── lib
│ ├── cmake
│ ├── libfunctional_k230.a
│ ├── libnncase.rt_modules.k230.a
│ └── libNncase.Runtime.Native.a
└── rvvlib
├── include
│ ├── k230_math.h
│ ├── nms.h
│ └── rvv_math.h
└── librvv.a
8 directories, 8 files
4.2 APIs#
4.2.1 hrt::create#
Description:
Creates a runtime_tensor.
Definition:
(1) NNCASE_API result<runtime_tensor> create(typecode_t datatype, dims_t shape, memory_pool_t pool = pool_shared_first) noexcept;
(2) NNCASE_API result<runtime_tensor> create(typecode_t datatype, dims_t shape, gsl::span<gsl::byte> data, bool copy,
memory_pool_t pool = pool_shared_first) noexcept;
(3) NNCASE_API result<runtime_tensor> create(typecode_t datatype, dims_t shape, strides_t strides, gsl::span<gsl::byte> data, bool copy, memory_pool_t pool = pool_shared_first, uintptr_t physical_address = 0) noexcept;
[Parameters]
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
datatype |
typecode_t |
Data type, e.g., dt_float32, dt_uint8 |
shape |
dims_t |
Shape of the tensor |
data |
gsl::span<gsl::byte> |
User data buffer |
copy |
bool |
Whether to copy |
pool |
memory_pool_t |
Memory pool type, default is pool_shared_first |
physical_address |
uintptr_t |
Physical address specified by the user |
[Return Value]
result<runtime_tensor>
Example:
// create input tensor
auto input_desc = interp.input_desc(0);
auto input_shape = interp.input_shape(0);
auto input_tensor = host_runtime_tensor::create(input_desc.datatype, input_shape, hrt::pool_shared).expect("cannot create input tensor");
4.2.2 hrt::sync#
Description:
Synchronizes the cache of the tensor.
For user input data, this interface’s
sync_write_backshould be called to ensure the data is flushed to DDR.For GNNE/AI2D computation output data, the GNNE/AI2D runtime has already performed
sync_invalidateby default.
Definition:
NNCASE_API result<void> sync(runtime_tensor &tensor, sync_op_t op, bool force = false) noexcept;
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
tensor |
runtime_tensor |
The tensor to operate on |
op |
sync_op_t |
|
force |
bool |
Whether to force execution |
Return Value:
result<void>
Example:
hrt::sync(input_tensor, sync_op_t::sync_write_back, true).expect("sync write_back failed");
4.2.3 interpreter::load_model#
Description:
Loads a kmodel.
Definition:
NNCASE_NODISCARD result<void> load_model(gsl::span<const gsl::byte> buffer) noexcept;
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
buffer |
gsl::span <const gsl::byte> |
kmodel buffer |
Return Value:
result<void>
Example:
interpreter interp;
auto model = read_binary_file<unsigned char>(kmodel);
interp.load_model({(const gsl::byte *)model.data(), model.size()}).expect("cannot load model.");
4.2.4 interpreter::inputs_size#
Description:
Gets the number of model inputs.
Definition:
size_t inputs_size() const noexcept;
Parameters:
None
Return Value:
size_t
Example:
auto inputs_size = interp.inputs_size();
4.2.5 interpreter::outputs_size#
Description:
Gets the number of model outputs.
Definition:
size_t outputs_size() const noexcept;
Parameters:
None
Return Value:
size_t
Example:
auto outputs_size = interp.outputs_size();
4.2.6 interpreter::input_shape#
Description:
Gets the shape of the specified input.
Definition:
const runtime_shape_t &input_shape(size_t index) const noexcept;
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
index |
size_t |
Index of the input |
Return Value:
runtime_shape_t
Example:
auto shape = interp.input_shape(0);
4.2.7 interpreter::output_shape#
Description:
Gets the shape of the specified output.
Definition:
const runtime_shape_t &output_shape(size_t index) const noexcept;
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
index |
size_t |
Index of the output |
Return Value:
runtime_shape_t
Example:
auto shape = interp.output_shape(0);
4.2.8 interpreter::input_tensor#
Description:
Gets/Sets the input tensor at the specified index.
Definition:
(1) result<runtime_tensor> input_tensor(size_t index) noexcept;
(2) result<void> input_tensor(size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) noexcept;
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
index |
size_t |
Index of the input |
tensor |
runtime_tensor |
The runtime tensor for input |
Return Value:
(1) result<runtime_tensor>
(2) result<void>
Example:
// set input
interp.input_tensor(0, input_tensor).expect("cannot set input tensor");
4.2.9 interpreter::output_tensor#
Description:
Gets/Sets the output tensor at the specified index.
Definition:
(1) result<runtime_tensor> output_tensor(size_t index) noexcept;
(2) result<void> output_tensor(size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) noexcept;
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
index |
size_t |
Index of the output |
tensor |
runtime_tensor |
The runtime tensor for output |
Return Value:
(1) result<runtime_tensor>
(2) result<void>
Example:
// get output
auto output_tensor = interp.output_tensor(0).expect("cannot get output tensor");
4.2.10 interpreter::run#
Description:
Executes KPU computation.
Definition:
result<void> run() noexcept;
Parameters:
None
Return Value:
result<void>
Example:
// run
interp.run().expect("error occurred in running model");
4.3 Example#
#include <chrono>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <nncase/runtime/interpreter.h>
#include <nncase/runtime/runtime_op_utility.h>
#define USE_OPENCV 1
#define preprocess 1
#if USE_OPENCV
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#endif
using namespace nncase;
using namespace nncase::runtime;
using namespace nncase::runtime::detail;
#define INPUT_HEIGHT 224
#define INPUT_WIDTH 224
#define INPUT_CHANNELS 3
template <class T>
std::vector<T> read_binary_file(const std::string &file_name)
{
std::ifstream ifs(file_name, std::ios::binary);
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.end);
size_t len = ifs.tellg();
std::vector<T> vec(len / sizeof(T), 0);
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.beg);
ifs.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(vec.data()), len);
ifs.close();
return vec;
}
void read_binary_file(const char *file_name, char *buffer)
{
std::ifstream ifs(file_name, std::ios::binary);
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.end);
size_t len = ifs.tellg();
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.beg);
ifs.read(buffer, len);
ifs.close();
}
static std::vector<std::string> read_txt_file(const char *file_name)
{
std::vector<std::string> vec;
vec.reserve(1024);
std::ifstream fp(file_name);
std::string label;
while (getline(fp, label))
{
vec.push_back(label);
}
return vec;
}
template<typename T>
static int softmax(const T* src, T* dst, int length)
{
const T alpha = *std::max_element(src, src + length);
T denominator{ 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
dst[i] = std::exp(src[i] - alpha);
denominator += dst[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
dst[i] /= denominator;
}
return 0;
}
#if USE_OPENCV
std::vector<uint8_t> hwc2chw(cv::Mat &img)
{
std::vector<uint8_t> vec;
std::vector<cv::Mat> rgbChannels(3);
cv::split(img, rgbChannels);
for (auto i = 0; i < rgbChannels.size(); i++)
{
std::vector<uint8_t> data = std::vector<uint8_t>(rgbChannels[i].reshape(1, 1));
vec.insert(vec.end(), data.begin(), data.end());
}
return vec;
}
#endif
static int inference(const char *kmodel_file, const char *image_file, const char *label_file)
{
// load kmodel
interpreter interp;
// Load kmodel from memory
auto kmodel = read_binary_file<unsigned char>(kmodel_file);
interp.load_model({ (const gsl::byte *)kmodel.data(), kmodel.size() }).expect("cannot load kmodel.");
// Load kmodel from file stream
std::ifstream ifs(kmodel_file, std::ios::binary);
interp.load_model(ifs).expect("cannot load kmodel");
// create input tensor
auto input_desc = interp.input_desc(0);
auto input_shape = interp.input_shape(0);
auto input_tensor = host_runtime_tensor::create(input_desc.datatype, input_shape, hrt::pool_shared).expect("cannot create input tensor");
interp.input_tensor(0, input_tensor).expect("cannot set input tensor");
// create output tensor
// auto output_desc = interp.output_desc(0);
// auto output_shape = interp.output_shape(0);
// auto output_tensor = host_runtime_tensor::create(output_desc.datatype, output_shape, hrt::pool_shared).expect("cannot create output tensor");
// interp.output_tensor(0, output_tensor).expect("cannot set output tensor");
// set input data
auto dst = input_tensor.impl()->to_host().unwrap()->buffer().as_host().unwrap().map(map_access_::map_write).unwrap().buffer();
#if USE_OPENCV
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(image_file);
cv::resize(img, img, cv::Size(INPUT_WIDTH, INPUT_HEIGHT), cv::INTER_NEAREST);
auto input_vec = hwc2chw(img);
memcpy(reinterpret_cast<char *>(dst.data()), input_vec.data(), input_vec.size());
#else
read_binary_file(image_file, reinterpret_cast<char *>(dst.data()));
#endif
hrt::sync(input_tensor, sync_op_t::sync_write_back, true).expect("sync write_back failed");
// run
size_t counter = 1;
auto start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
for (size_t c = 0; c < counter; c++)
{
interp.run().expect("error occurred in running model");
}
auto stop = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
double duration = std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>(stop - start).count();
std::cout << "interp.run() took: " << duration / counter << " ms" << std::endl;
// get output data
auto output_tensor = interp.output_tensor(0).expect("cannot set output tensor");
dst = output_tensor.impl()->to_host().unwrap()->buffer().as_host().unwrap().map(map_access_::map_read).unwrap().buffer();
float *output_data = reinterpret_cast<float *>(dst.data());
auto out_shape = interp.output_shape(0);
auto size = compute_size(out_shape);
// postprocess softmax by cpu
std::vector<float> softmax_vec(size, 0);
auto buf = softmax_vec.data();
softmax(output_data, buf, size);
auto it = std::max_element(buf, buf + size);
size_t idx = it - buf;
// load label
auto labels = read_txt_file(label_file);
std::cout << "image classify result: " << labels[idx] << "(" << *it << ")" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::cout << "case " << argv[0] << " built at " << __DATE__ << " " << __TIME__ << std::endl;
if (argc != 4)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <kmodel> <image> <label>" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
int ret = inference(argv[1], argv[2], argv[3]);
if (ret)
{
std::cerr << "inference failed: ret = " << ret << std::endl;
return -2;
}
return 0;
}
5. AI2D Runtime APIs (C++)#
5.1 Introduction#
AI2D Runtime APIs are used to configure AI2D parameters on AI devices, generate related register configurations, execute AI2D computations, etc. Please read the last section Precautions before use.
5.1.1 Supported Format Conversions#
Input Format |
Output Format |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|
YUV420_NV12 |
RGB_planar/YUV420_NV12 |
|
YUV420_NV21 |
RGB_planar/YUV420_NV21 |
|
YUV420_I420 |
RGB_planar/YUV420_I420 |
|
YUV400 |
YUV400 |
|
NCHW(RGB_planar) |
NCHW(RGB_planar) |
|
RGB_packed |
RGB_planar/RGB_packed |
|
RAW16 |
RAW16/8 |
Depth map, performs shift operation |
5.1.2 Function Descriptions#
Function |
Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|
Affine Transformation |
Supports input formats YUV420, YUV400, RGB (planar/packed); supports depth map RAW16 format; supports output formats YUV400, RGB, depth map |
|
Crop/Resize/Padding |
Supports input YUV420, YUV400, RGB; supports depth map RAW16 format; Resize supports intermediate NCHW arrangement format; supports output formats YUV420, YUV400, RGB |
Only supports constant padding |
Shift |
Supports input format Raw16; supports output format Raw8 |
|
Sign Bit |
Supports signed and unsigned input |
5.2 APIs#
5.2.1 ai2d_format#
Description:
ai2d_format is used to configure the optional data formats for input and output.
Definition:
enum class ai2d_format
{
YUV420_NV12 = 0,
YUV420_NV21 = 1,
YUV420_I420 = 2,
NCHW_FMT = 3,
RGB_packed = 4,
RAW16 = 5,
};
5.2.2 ai2d_interp_method#
Description:
ai2d_interp_method is used to configure the optional interpolation methods.
Definition:
enum class ai2d_interp_method
{
tf_nearest = 0,
tf_bilinear = 1,
cv2_nearest = 2,
cv2_bilinear = 3,
};
5.2.3 ai2d_interp_mode#
Description:
ai2d_interp_mode is used to configure the optional interpolation modes.
Definition:
enum class ai2d_interp_mode
{
none = 0,
align_corner = 1,
half_pixel = 2,
};
5.2.4 ai2d_pad_mode#
Description:
ai2d_pad_mode is used to configure the optional padding modes. Currently, only constant padding is supported.
Definition:
enum class ai2d_pad_mode
{
constant = 0,
copy = 1,
mirror = 2,
};
5.2.5 ai2d_datatype_t#
Description:
ai2d_datatype_t is used to set the data types during the AI2D computation process.
Definition:
struct ai2d_datatype_t
{
ai2d_format src_format;
ai2d_format dst_format;
datatype_t src_type;
datatype_t dst_type;
ai2d_data_loc src_loc = ai2d_data_loc::ddr;
ai2d_data_loc dst_loc = ai2d_data_loc::ddr;
}
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
src_format |
ai2d_format |
Input data format |
dst_format |
ai2d_format |
Output data format |
src_type |
datatype_t |
Input data type |
dst_type |
datatype_t |
Output data type |
src_loc |
ai2d_data_loc |
Input data location, default is DDR |
dst_loc |
ai2d_data_loc |
Output data location, default is DDR |
Example:
ai2d_datatype_t ai2d_dtype { ai2d_format::RAW16, ai2d_format::NCHW_FMT, datatype_t::dt_uint16, datatype_t::dt_uint8 };
5.2.6 ai2d_crop_param_t#
Description:
ai2d_crop_param_t is used to configure parameters related to cropping.
Definition:
struct ai2d_crop_param_t
{
bool crop_flag = false;
int32_t start_x = 0;
int32_t start_y = 0;
int32_t width = 0;
int32_t height = 0;
}
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
crop_flag |
bool |
Whether to enable cropping |
start_x |
int |
Starting pixel in the width direction |
start_y |
int |
Starting pixel in the height direction |
width |
int |
Crop length in the width direction |
height |
int |
Crop length in the height direction |
Example:
ai2d_crop_param_t crop_param { true, 40, 30, 400, 600 };
5.2.7 ai2d_shift_param_t#
Description:
ai2d_shift_param_t is used to configure parameters related to shifting.
Definition:
struct ai2d_shift_param_t
{
bool shift_flag = false;
int32_t shift_val = 0;
}
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
shift_flag |
bool |
Whether to enable shifting |
shift_val |
int |
Number of bits to shift right |
Example:
ai2d_shift_param_t shift_param { true, 2 };
5.2.8 ai2d_pad_param_t#
Description:
ai2d_pad_param_t is used to configure parameters related to padding.
Definition:
struct ai2d_pad_param_t
{
bool pad_flag = false;
runtime_paddings_t paddings;
ai2d_pad_mode pad_mode = ai2d_pad_mode::constant;
std::vector<int32_t> pad_val; // by channel
}
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
pad_flag |
bool |
Whether to enable padding |
paddings |
runtime_paddings_t |
Padding for each dimension, shape= |
pad_mode |
ai2d_pad_mode |
Padding mode, only constant padding is supported |
pad_val |
std::vector<int32_t> |
Padding value for each channel |
Example:
ai2d_pad_param_t pad_param { false, { { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 60, 60 } }, ai2d_pad_mode::constant, { 255 } };
5.2.9 ai2d_resize_param_t#
Description:
ai2d_resize_param_t is used to configure parameters related to resizing.
Definition:
struct ai2d_resize_param_t
{
bool resize_flag = false;
ai2d_interp_method interp_method = ai2d_interp_method::tf_bilinear;
ai2d_interp_mode interp_mode = ai2d_interp_mode::none;
}
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
resize_flag |
bool |
Whether to enable resizing |
interp_method |
ai2d_interp_method |
Interpolation method for resizing |
interp_mode |
ai2d_interp_mode |
Resize mode |
Example:
ai2d_resize_param_t resize_param { true, ai2d_interp_method::tf_bilinear, ai2d_interp_mode::half_pixel };
5.2.10 ai2d_affine_param_t#
Description:
ai2d_affine_param_t is used to configure parameters related to affine transformations.
Definition:
struct ai2d_affine_param_t
{
bool affine_flag = false;
ai2d_interp_method interp_method = ai2d_interp_method::cv2_bilinear;
uint32_t cord_round = 0;
uint32_t bound_ind = 0;
int32_t bound_val = 0;
uint32_t bound_smooth = 0;
std::vector<float> M;
}
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
affine_flag |
bool |
Whether to enable affine transformations |
interp_method |
ai2d_interp_method |
Interpolation method used for affine transformations |
cord_round |
uint32_t |
Integer boundary, 0 or 1 |
bound_ind |
uint32_t |
Boundary pixel mode, 0 or 1 |
bound_val |
uint32_t |
Boundary fill value |
bound_smooth |
uint32_t |
Boundary smoothing, 0 or 1 |
M |
std::vector<float> |
Vector corresponding to the affine transformation matrix. For affine transformation $Y=[a_0, a_1; a_2, a_3] \cdot X + [b_0, b_1]$, $M={a_0,a_1,b_0,a_2,a_3,b_1}$ |
Example:
ai2d_affine_param_t affine_param { true, ai2d_interp_method::cv2_bilinear, 0, 0, 127, 1, { 0.5, 0.1, 0.0, 0.1, 0.5, 0.0 } };
5.2.11 ai2d_builder::ai2d_builder#
Description:
Constructor for ai2d_builder.
Definition:
ai2d_builder(dims_t &input_shape, dims_t &output_shape, ai2d_datatype_t ai2d_dtype, ai2d_crop_param_t crop_param, ai2d_shift_param_t shift_param, ai2d_pad_param_t pad_param, ai2d_resize_param_t resize_param, ai2d_affine_param_t affine_param);
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
input_shape |
dims_t |
Input shape |
output_shape |
dims_t |
Output shape |
ai2d_dtype |
ai2d_datatype_t |
AI2D data type |
crop_param |
ai2d_crop_param_t |
Crop parameters |
shift_param |
ai2d_shift_param_t |
Shift parameters |
pad_param |
ai2d_pad_param_t |
Pad parameters |
resize_param |
ai2d_resize_param_t |
Resize parameters |
affine_param |
ai2d_affine_param_t |
Affine parameters |
Return Value:
None
Example:
dims_t in_shape { 1, ai2d_input_c_, ai2d_input_h_, ai2d_input_w_ };
auto out_span = ai2d_out_tensor_.shape();
dims_t out_shape { out_span.begin(), out_span.end() };
ai2d_datatype_t ai2d_dtype { ai2d_format::NCHW_FMT, ai2d_format::NCHW_FMT, typecode_t::dt_uint8, typecode_t::dt_uint8 };
ai2d_crop_param_t crop_param { false, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
ai2d_shift_param_t shift_param { false, 0 };
ai2d_pad_param_t pad_param { true, { { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 70, 70 } }, ai2d_pad_mode::constant, { 0, 0, 0 } };
ai2d_resize_param_t resize_param { true, ai2d_interp_method::tf_bilinear, ai2d_interp_mode::half_pixel };
ai2d_affine_param_t affine_param { false };
ai2d_builder_.reset(new ai2d_builder(in_shape, out_shape, ai2d_dtype, crop_param, shift_param, pad_param, resize_param, affine_param));
5.2.12 ai2d_builder::build_schedule#
Description:
Generates the parameters required for AI2D computation.
Definition:
result<void> build_schedule();
Parameters:
None
Return Value:
result<void>
Example:
ai2d_builder_->build_schedule();
5.2.13 ai2d_builder::invoke#
Description:
Configures the registers and starts the AI2D computation.
Definition:
result<void> invoke(runtime_tensor &input, runtime_tensor &output);
Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor |
Input tensor |
output |
runtime_tensor |
Output tensor |
Return Value:
result<void>
Example:
// run ai2d
ai2d_builder_->invoke(ai2d_in_tensor, ai2d_out_tensor_).expect("error occurred in ai2d running");
5.3 Example#
static void test_pad_mini_test(const char *gmodel_file, const char *expect_file)
{
// input tensor
dims_t in_shape { 1, 100, 150, 3 };
auto in_tensor = host_runtime_tensor::create(dt_uint8, in_shape, hrt::pool_shared).expect("cannot create input tensor");
auto mapped_in_buf = std::move(hrt::map(in_tensor, map_access_t::map_write).unwrap());
read_binary_file(gmodel_file, reinterpret_cast<char *>(mapped_in_buf.buffer().data()));
mapped_in_buf.unmap().expect("unmap input tensor failed");
hrt::sync(in_tensor, sync_op_t::sync_write_back, true).expect("write back input failed");
// output tensor
dims_t out_shape { 1, 100, 160, 3 };
auto out_tensor = host_runtime_tensor::create(dt_uint8, out_shape, hrt::pool_shared).expect("cannot create output tensor");
// config ai2d
ai2d_datatype_t ai2d_dtype { ai2d_format::RGB_packed, ai2d_format::RGB_packed, dt_uint8, dt_uint8 };
ai2d_crop_param_t crop_param { false, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
ai2d_shift_param_t shift_param { false, 0 };
ai2d_pad_param_t pad_param { true, { { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 10, 0 } }, ai2d_pad_mode::constant, { 255, 10, 5 } };
ai2d_resize_param_t resize_param { false, ai2d_interp_method::tf_bilinear, ai2d_interp_mode::half_pixel };
ai2d_affine_param_t affine_param { false };
// run
ai2d_builder builder { in_shape, out_shape, ai2d_dtype, crop_param, shift_param, pad_param, resize_param, affine_param };
auto start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
builder.build_schedule().expect("error occurred in ai2d build_schedule");
builder.invoke(in_tensor, out_tensor).expect("error occurred in ai2d invoke");
auto stop = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
double duration = std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>(stop - start).count();
std::cout << "ai2d run: duration = " << duration << " ms, fps = " << 1000 / duration << std::endl;
// compare
auto mapped_out_buf = std::move(hrt::map(out_tensor, map_access_t::map_read).unwrap());
auto actual = mapped_out_buf.buffer().data();
auto expected = read_binary_file<unsigned char>(expect_file);
int ret = memcmp(reinterpret_cast<void *>(actual), reinterpret_cast<void *>(expected.data()), expected.size());
if (!ret)
{
std::cout << "compare output succeed!" << std::endl;
}
else
{
auto cos = cosine(reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t *>(actual), reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t *>(expected.data()), expected.size());
std::cerr << "compare output failed: cosine similarity = " << cos << std::endl;
}
}
5.4 Notes#
Affine and Resize functions are mutually exclusive and cannot be enabled simultaneously.
The input format for the Shift function can only be Raw16.
The pad value is configured per channel, and the number of elements in the list should be equal to the number of channels.
In the current version, when only one AI2D function is needed, other parameters also need to be configured, with the flag set to false, and other fields do not need to be configured.
When configuring multiple functions, the execution order is Crop->Shift->Resize/Affine->Pad. Ensure the parameters match accordingly.