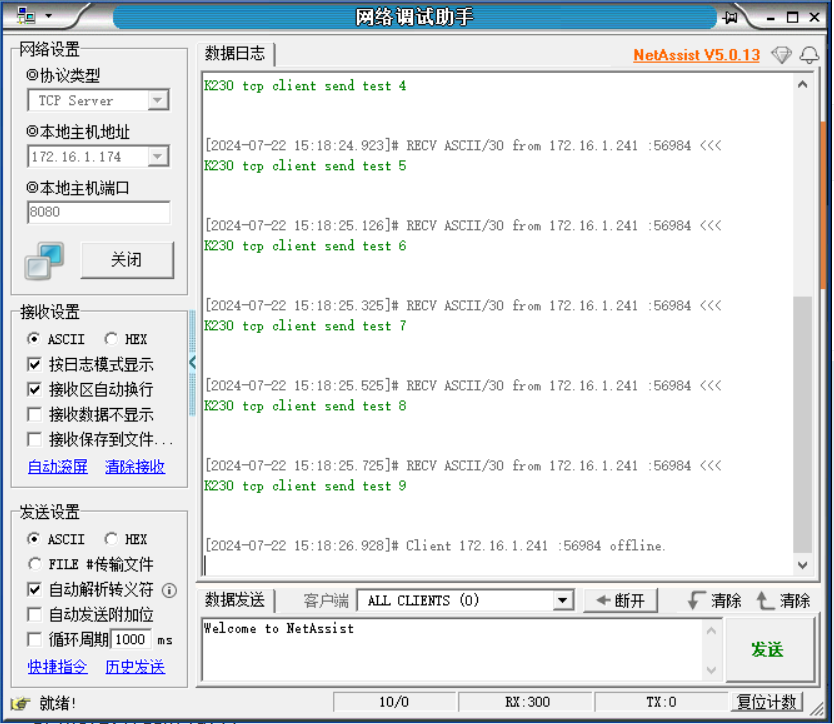
3. TCP-Client Example Explanation#
1. Environment Preparation#
To ensure a smooth demonstration of TCP communication, we need to confirm that the following environment is correctly configured:
1.1 Hardware Connection#
Ensure that your CanMV development board and computer are connected to the same router or switch via an Ethernet cable to form a local area network.
Ensure the router or switch is working properly to guarantee network connection stability.
1.2 Disable Firewall#
To avoid the firewall blocking TCP communication, it is recommended to temporarily disable the computer’s firewall.
1.3 Tool Preparation#
Download and install NetAssist Network Debugging Assistant as a network communication testing tool to help send and receive network data.
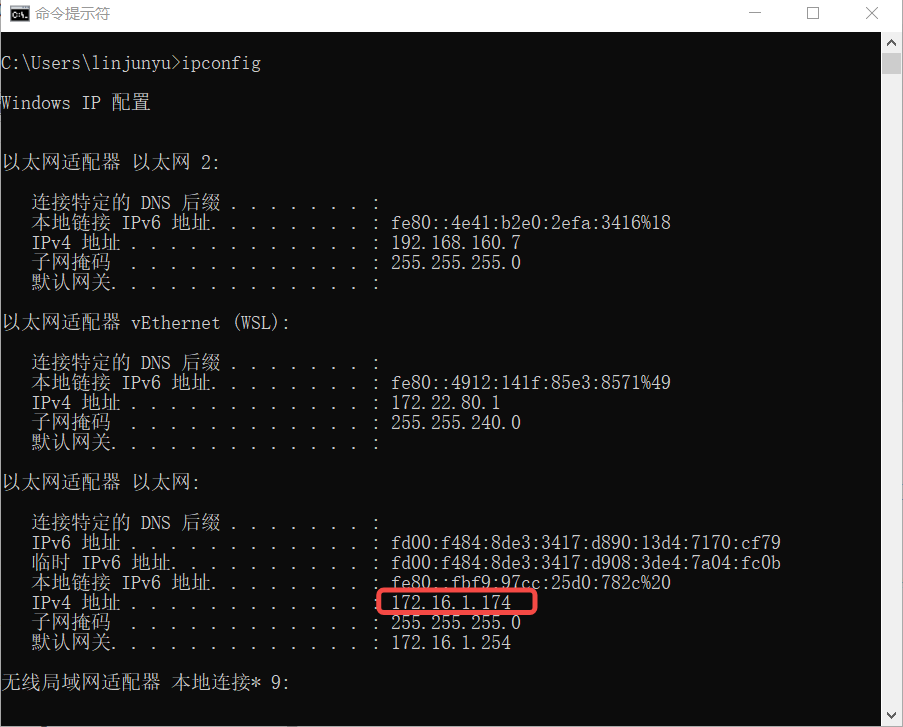
1.4 Obtain IP Address#
Open the Command Prompt (CMD), enter
ipconfig, and query and record the IP address of the computer’s network card for subsequent configuration and testing.
2. Client Code Analysis#
2.1 Import Necessary Libraries#
import network
import socket
import time
network: Used for network interface operations, such as configuring IP addresses and checking network status.
socket: Provides the Socket interface for network communication.
time: Provides functions related to time, such as delay (
sleep).
2.2 Define Client Function#
def client():
# ... (subsequent code)
The
clientfunction contains the main logic of the TCP client.
2.3 Configure Network Interface#
def network_use_wlan(is_wlan=True):
if is_wlan:
sta = network.WLAN(0)
sta.connect("Canaan", "Canaan314")
print(sta.status())
while sta.ifconfig()[0] == '0.0.0.0':
os.exitpoint()
print(sta.ifconfig())
ip = sta.ifconfig()[0]
return ip
else:
a = network.LAN()
if not a.active():
raise RuntimeError("LAN interface is not active.")
a.ifconfig("dhcp")
print(a.ifconfig())
ip = a.ifconfig()[0]
return ip
Configure the network interface based on the parameters, as follows:
WLAN Mode:
If
is_wlan=True, configure the wireless network interface (WLAN) and connect to the Wi-Fi with SSID “Canaan” and password “Canaan314”.Wait and check if a valid IP address is assigned, then return the IP.
LAN Mode:
If
is_wlan=False, configure the wired network interface (LAN), enable DHCP to automatically obtain an IP address, and return the IP.
2.4 Create Socket#
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
Create a Socket object using IPv4 (
AF_INET) and TCP (SOCK_STREAM) protocol.
2.5 Obtain Server Address and Port#
ai = socket.getaddrinfo("172.16.1.174", 8080)
addr = ai[0][-1] # Extract address and port
Use
getaddrinfoto obtain the server’s IP address and port number, and extract the address information.
2.6 Connect to Server#
try:
s.connect(addr)
print("Connected to server:", addr)
except Exception as e:
s.close()
print("Connection error:", e)
return
Try to connect to the server. If the connection fails, print the error message and close the connection.
2.7 Send Data#
for i in range(10):
message = "K230 TCP client send test {0} \r\n".format(i)
print("Sending:", message)
s.sendall(message.encode())
time.sleep(0.2)
Send 10 test messages in a loop, using the
sendallmethod to ensure each message is completely sent.
2.8 Close Socket#
s.close()
print("Client ends connection.")
Close the Socket to release resources, indicating the client has ended the connection.
2.9 Complete Code Example#
import network
import socket
import os, time
def network_use_wlan(is_wlan=True):
if is_wlan:
sta = network.WLAN(0)
sta.connect("Canaan", "Canaan314")
print(sta.status())
while sta.ifconfig()[0] == '0.0.0.0':
os.exitpoint()
print(sta.ifconfig())
ip = sta.ifconfig()[0]
return ip
else:
a = network.LAN()
if not a.active():
raise RuntimeError("LAN interface is not active.")
a.ifconfig("dhcp")
print(a.ifconfig())
ip = a.ifconfig()[0]
return ip
def client():
network_use_wlan(True)
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
ai = socket.getaddrinfo("192.168.1.110", 8080)
print("Address infos:", ai)
addr = ai[0][-1]
print("Connecting to:", addr)
try:
s.connect(addr)
except Exception as e:
s.close()
print("Connection error:", e)
return
for i in range(10):
message = "K230 TCP client send test {0} \r\n".format(i)
print("Sending:", message)
s.sendall(message.encode())
time.sleep(0.2)
s.close()
print("Connection closed.")
client()
3. Running Results and Operation Instructions#
Open the NetAssist Network Debugging Assistant, configure it as a TCP server, and wait for the connection:
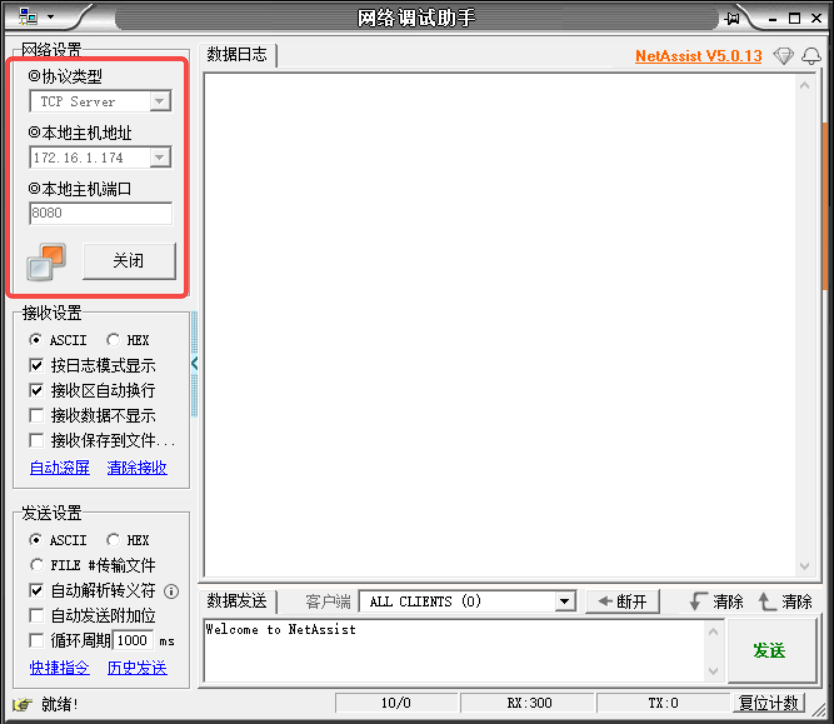
Modify the server’s IP and port number in the code:
ai = socket.getaddrinfo("172.16.1.174", 8080)
Run the client code, and NetAssist will display the messages sent by the client: