K230 SDK CanMV Board Demo User Guide#

Copyright 2023 Canaan Inc. ©
Disclaimer#
The products, services or features you purchase should be subject to Canaan Inc. (“Company”, hereinafter referred to as “Company”) and its affiliates are bound by the commercial contracts and terms and conditions of all or part of the products, services or features described in this document may not be covered by your purchase or use. Unless otherwise agreed in the contract, the Company does not provide any express or implied representations or warranties as to the correctness, reliability, completeness, merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose and non-infringement of any statements, information, or content in this document. Unless otherwise agreed, this document is intended as a guide for use only.
Due to product version upgrades or other reasons, the content of this document may be updated or modified from time to time without any notice.
Trademark Notice#
 , “Canaan” and other Canaan trademarks are trademarks of Canaan Inc. and its affiliates. All other trademarks or registered trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are owned by their respective owners.
, “Canaan” and other Canaan trademarks are trademarks of Canaan Inc. and its affiliates. All other trademarks or registered trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are owned by their respective owners.
Copyright 2023 Canaan Inc.. © All Rights Reserved. Without the written permission of the company, no unit or individual may extract or copy part or all of the content of this document without authorization, and shall not disseminate it in any form.
Directory#
[TOC]
preface#
Overview#
This document mainly introduces the demo program provided in the K230 SDK to adapt to the Canmv-K230 development board.
Reader object#
This document (this guide) is intended primarily for:
Technical Support Engineer
Software Development Engineer
Definition of acronyms#
abbreviation |
illustrate |
|---|---|
UVC |
USB video class(USB Camera) |
VVI |
Virtual Video Input, which mainly used for pipeline debugging |
Revision history#
Document version number |
Modify the description |
Author |
date |
|---|---|---|---|
V1.0 |
Initial |
System Software Department |
2023-10-11 |
1. Overview#
This document describes the demo functions and usage methods provided by the K230 SDK. The executable programs on rt-smart are compiled into /sharefs directory of the little core by default.When testing the big core program, you need to wait for the little core to be fully started, and then the big core enter the /sharefs/app directory to test. The audio and video resource files used in the test demos can be obtained at the following link address https://kendryte-download.canaan-creative.com/k230/downloads/test_resource/
2. Demo introduction#
2.1 Display_demo#
2.1.1 Introduction to display_demo#
VO (Video Output) module actively reads video and graphics data from the corresponding location in memory, and outputs video and graphics through the corresponding display device. Display/write-back devices, video layers, and graphics layer conditions supported by the chip.
2.1.2 Feature description#
Video ouput contains a use case, which is the test of inserting frames at the VO OSD layer
2.1.3 Dependent Resources#
Monitor with HDMI interface and HDMI cable, the display must support 1080P30, otherwise it cannot be displayed
2.1.4 Instructions for Use#
2.1.4.1 Compilation#
Software compilation refers to the README.md in the release SDK package
2.1.4.2 Execution#
VO OSD layer inserts frames
./sample_vo.elf 15
After executing the command, pressing Enter once will insert a solid green image, and press Enter again to exit
The display effect is as follows:
2.2 Venc_demo#
2.2.1 Introduction to Venc_demo#
Venc demo encodes the graphics received by vi, and can frame and OSD overlay the input image. The supported encoding protocols are H.264/H.265/JPEG. The encoding results can be stored as a file, exported to the local computer, and played back using video software.
2.2.2 Feature description#
Only 1280x720 resolution is supported.
2.2.3 Dependent Resources#
Camera
2.2.4 Instructions for Use#
2.2.4.1 mpp_demo Execution#
After execution./sample_venc.elf -h, the instructions for using the demo are output as follows:
Usage : ./sample_venc.elf [index] -sensor [sensor_index] -o [filename]
index:
0) H.265e.
1) JPEG encode.
2) OSD + H.264e.
3) OSD + Border + H.265e.
sensor_index: see vicap doc
sensor_index value refer to the k230_docs/en/01_software/board/mpp/K230_Camera_Sensor_Adaptation_Guide.mddescription of the k_vicap_sensor_type in the document, and the default value is 7
Example:
./sample_venc.elf 0 -sensor 7 -o out.265
2.2.4.2 MAPI encoding demo#
sample_venc default sensor type used is IMX335_MIPI_2LANE_RAW12_1920X1080_30FPS_LINEAR, the demo currently supports 3-way encoding, you can modify the sensor type and other parameters by passing parameters from the command line, the specific description is as follows:
After launching the board:
Use
lsmodto check whether the k_ipcm module is loaded on the little core side. If it is not loaded, executeinsmod k_ipcm.koto load the k_ipcm module.Start the internuclear communication process on the large nuclear side, execute
./sample_sys_inif.elfIn the /mnt directory on the little core side, execute ,
./sample_vencby default, 1-channel H264 video encoding is executed, the resolution is 1280x720, and the generated code stream file is stored under the /tmp directory
Usage: ./sample_venc -s 0 -n 2 -o /tmp -t 0
-s or --sensor_type [sensor_index],\n");
see vicap doc
-n or --chn_num [number], 1, 2, 3
-t or --type [type_index]
0: h264 type
1: h265 type
2: jpeg type
-o or --out_path [output_path]
-h or --help, will print usage
sensor_index value refer to the k230_docs/en/01_software/board/mpp/K230_Camera_Sensor_Adaptation_Guide.mddescription of the k_vicap_sensor_type in the document, and the default value is 7
Depending on the encoding type, different stream files will be generated in the output directory specified by the little core, for the H264 type, a file will be generated, where 0 represents 0 channel, ctrl+cfor the H265 type, a file of the form will be generated, and the same 0 will stream_chn0.264represent 0 channel; for the JPEG type, the shape will be generatedstream_chn0.265``chn0_0.jpgThe jpg image represents the 0th image of channel 0, and 10 jpg images will be generated by default.
2.2.4.3 View results#
The output file can be exported locally for viewing with video playback software.
2.3 Nonai_2d_demo#
2.3.1 Introduction to Nonai_2d_demo#
Nonai_2d demo implements the function of image overlay on the input file.
2.3.2 Feature description#
Nonai_2d performs image overlay operations by reading a YUV (I420 format) file.
2.3.3 Dependent Resources#
Not.
2.3.4 Instructions for Use#
The input parameters are as follows:
The parameter name |
description |
Default value |
|---|---|---|
-i |
Enter a file name |
- |
-in |
Image width |
- |
-h |
Image height |
- |
-or |
Output file name |
- |
2.3.4.1 Execution#
Example:
./sample_nonai_2d.elf -i /sharefs/foreman_128x64_3frames.yuv -w 128 -h 64 -o /sharefs/out_2d.yuv
2.3.4.2 View results#
The output file can be exported to the local computer for viewing with the YUV playback software.
2.4 Vdec_demo#
2.4.1 Introduction to Vdec_demo#
Vdec demo implements the function of video decoding. The decoding function supports H.264/H.265/JPEG decoding. The supported input data formats are .264/.265/.jpeg.
2.4.2 Feature description#
Vdec demos are decoded by reading stream files. The decoding output is displayed on the screen.
2.4.3 Dependent Resources#
Not.
2.4.4 Instructions for Use#
2.4.4.1 Execution#
Execute, ./sample_vdec.elf -helpyou can see the configurable parameters and descriptions, the default values of which are shown in the following table:
The parameter name |
illustrate |
Default value |
|---|---|---|
i |
Enter a file name, which needs to be suffixed .264/.265/.jpg |
- |
type |
vo connector type, please refer to vo document |
0 |
The type value is set to 0 in thek230_docs/en/01_software/board/mpp/K230_video_output_API_reference.md description of the k_connector_type
2.4.4.1.1 VDEC bound VO decoding display#
./sample_vdec.elf -type 1 -i canaan.264
2.4.4.1.2 MAPI VIDEC bound VO decoding display#
./sample_vdec.elf -type 1 -i canaan.264
2.4.4.2 View results#
The decoding result can be viewed on the screen.
2.5 Audio_demo#
2.5.1 Introduction to audio_demo#
Audio Demo implements audio input and output functions by calling API interfaces. The audio input and output use the I2S module. The demo includes use cases where audio input or audio output can be tested separately, as well as use cases where audio input and output can be tested at the same time.
2.5.2 Feature description#
2.5.2.1 Audio input#
Audio input analyzes whether it is normal by capturing sounds from the environment and saving them as files.
In the demo, 15S minutes of audio data is collected, and the file format collected is WAV, which can be played directly using VLC.
2.5.2.2 Audio output#
The audio output is judged by playing the WAV file, plugging in the headphones to listen to the sound.
In the demo, the audio output function is tested by playing WAV, and WAV files in different audio formats can be uploaded to test the audio output function.
2.5.2.3 Audio input and output#
Audio input and output can be tested at the same time.
Test the function of the I2S module, that is: real-time acquisition of sound in the environment through the I2S audio input and sound in the environment through the I2S audio output, and connect the headphones to hear the sound in the environment in real time.
2.5.2.4 Audio codec#
Built-in G711A/U 16bit audio codec, users can register other external codecs.
2.5.3 Instructions for Use#
2.5.3.1 Compilation#
For a detailed description of the software compilation environment, refer to the SDK
README.md.
2.5.3.2 Execution#
After entering the rt-smart system, enter the /sharefs/app directory tosample_audio.elf test the demo.
You can enter
./sample_audio.elf -helphow to view the demo.-typeoption to test different module functionality;-samplerateOption to configure audio input and output different sample rates (8K-192K), default is 44.1K;-enablecodecUse a built-in codec or off-chip audio daughter board;-loglevelPrint the kernel log level;-bitwidthSet audio sampling accuracy (16/24/32);-filenameLoad or store the WAV/G711 file name.
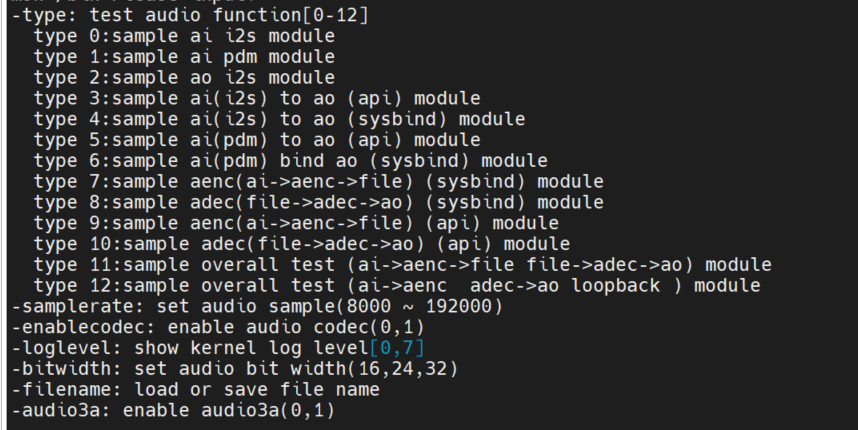
2.5.3.2.1 I2S audio input test#
Input
./sample_audio.elf -type 0to acquire PCM audio data in 15S-samplerateoption to choose to capture audio at different sample rates,-bitwidthto set different sampling accuracy,-enablecodecSet whether to use the built-in codec,-filenameSave the data to a file. After collecting 15s data, the demo automatically exits.
Demo implementation idea: This test collects data by calling the API function: AND in a loopkd_mpi_ai_get_frame``kd_mpi_ai_release_frame. Note that the AI dev number corresponding to i2s is 0.
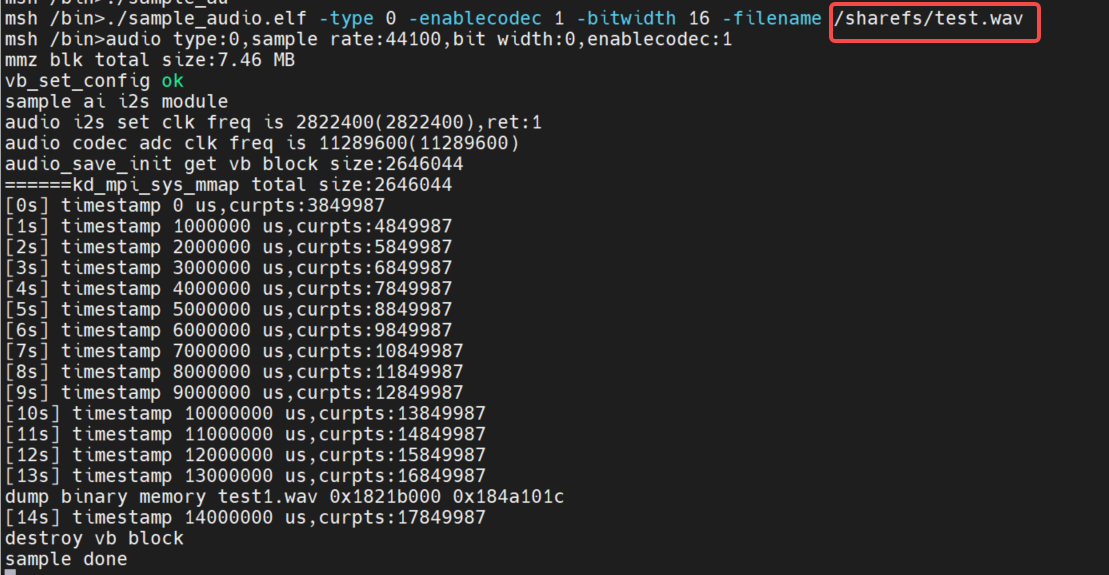
2.5.3.2.2 I2S audio output test#
To support playback of WAV files, you need to copy the WAV file to the sharefs path. The demo will loop the WAV file (any other WAV file can also be used), and the user can press any key to exit the function test.
Demo implementation idea: This test outputs sound in real time by calling API functions in a loopkd_mpi_ao_send_frame.
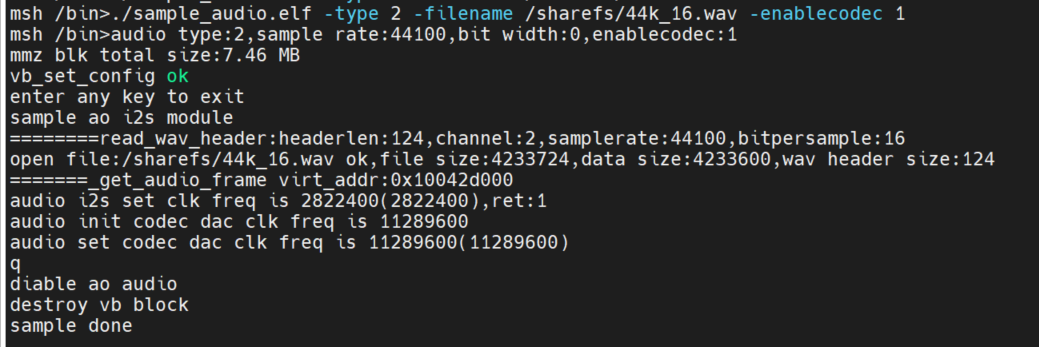
2.5.3.2.3 I2S audio input and output API interface test#
input./sample_audio.elf -type 3 -bitwidth 16, real-time test of audio input and output functions through API interface.
Test the overall functionality of audio input and output by calling the API interface:kd_mpi_ai_get_frame Obtain audio data and call kd_mpi_ao_send_frameoutput audio data. The user can press any key to exit the feature test. During the test, the timestamp information collected by AI is output in real time.
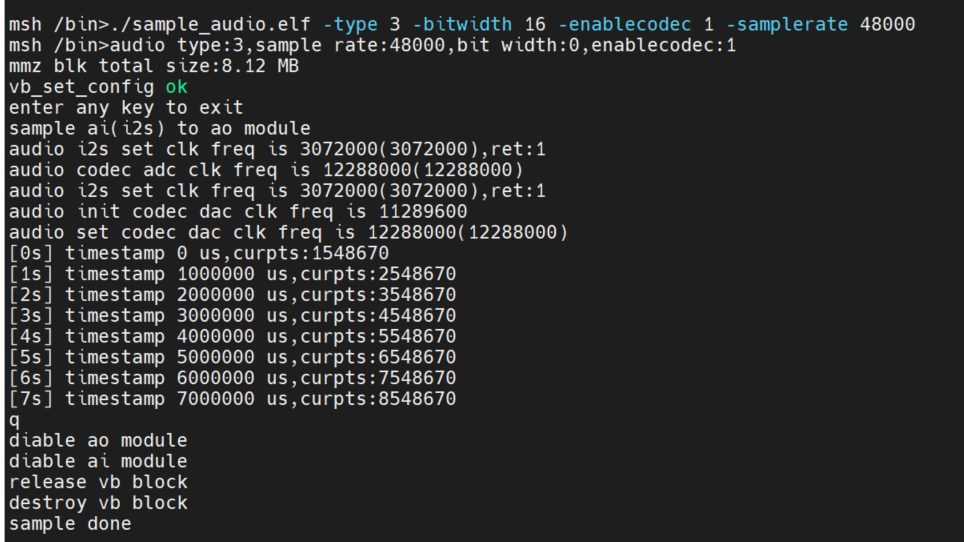
2.5.3.2.4 System binding test for I2S audio input and output modules#
Input./sample_audio.elf -type 4, real-time test of audio input and output functions through AI and AO module binding.
By calling the system binding API interface: kd_mpi_sys_bindbind the AI and AO modules to test the overall function of audio input and output. The user can press any key to exit the feature test.
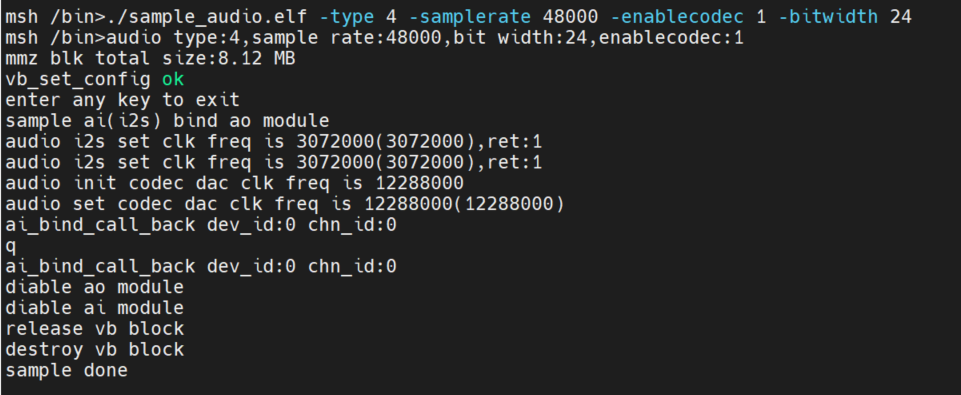
2.5.3.2.5 Coding Tests#
Get AI data and encode it and save it to a file. The codec only supports G711A/U, 16bit.
System binding method:./sample_audio.elf -type 7 -bitwidth 16 -enablecodec 1 -filename /sharefs/i2s_codec.g711a
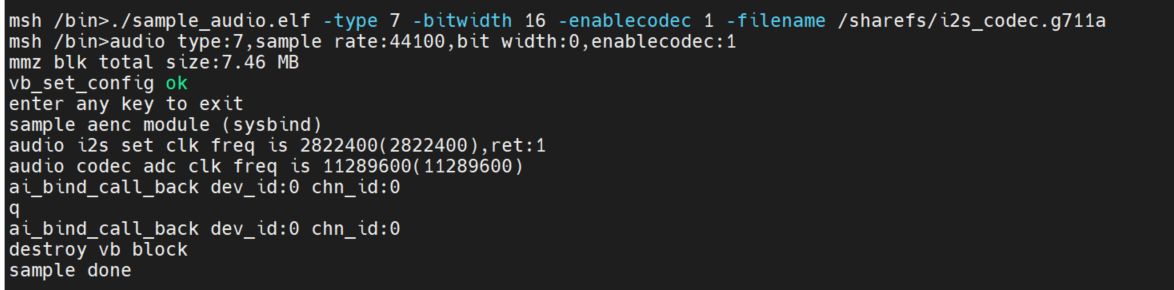
API interface mode:./sample_audio.elf -type 9 -bitwidth 16 -enablecodec 1 -filename /sharefs/i2s_codec.g711a
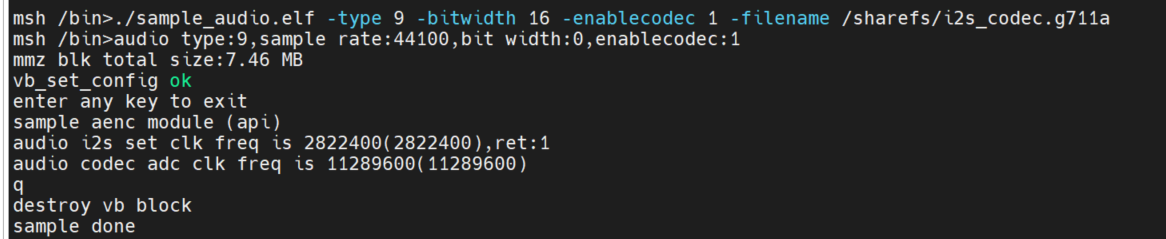
2.5.3.2.6 Decoding test#
Read file data and decode playback. The codec only supports G711A/U, 16bit.
System binding method:./sample_audio.elf -type 8 -filename /sharefs/gyz.g711a -enablecodec 1 -bitwidth 16
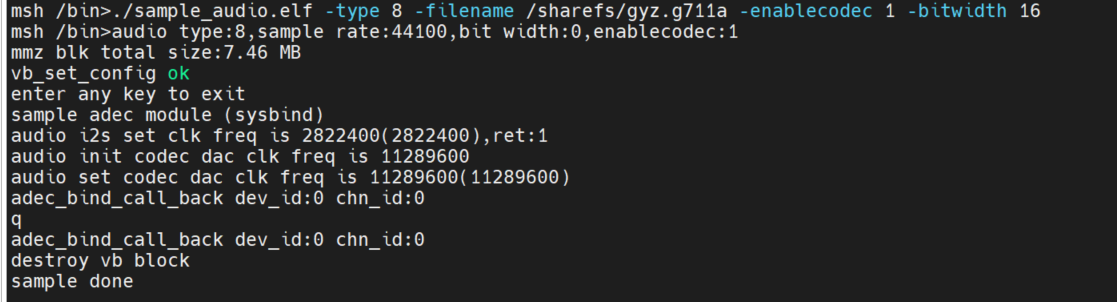
API interface mode:./sample_audio.elf -type 10 -filename /sharefs/gyz.g711a -enablecodec 1 -bitwidth 16
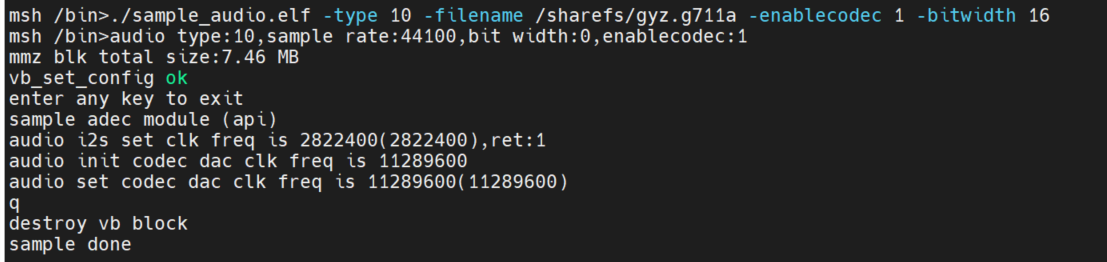
2.5.3.2.7 Audio full-process test#
The recording module ai->aenc->file and the playback module file->adec->ao two links run at the same time, simulating the scene of voice intercom. Using the built-in codec, 16-bit precision to simulate.
-filenameto select the file to be played, for G711A format, select-sampleratethe sampling accuracy. Recording file name: +: if -_recfilename is -filename/sharefs/test.g711a, the recording file name is:/sharefs/test.g711a_rec
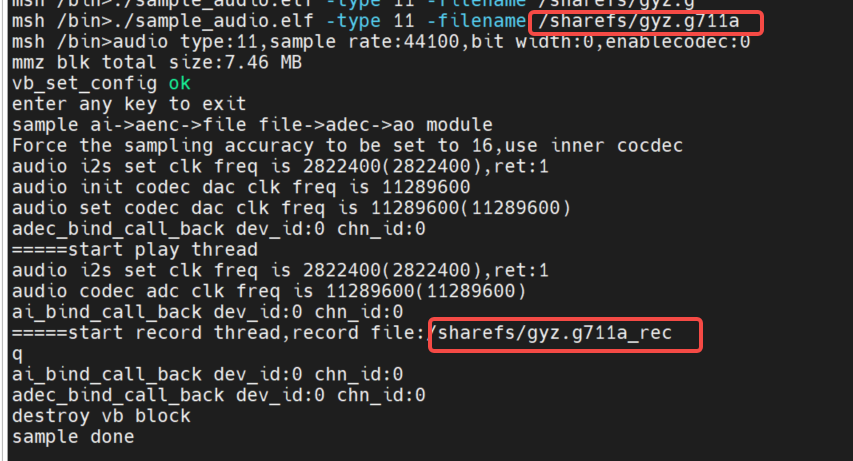
2.AI->AENC, ADC->AO two links are bound loopback test. Using the built-in codec, 16-bit precision to simulate.
Also test the G711 encoded stream timestamp.
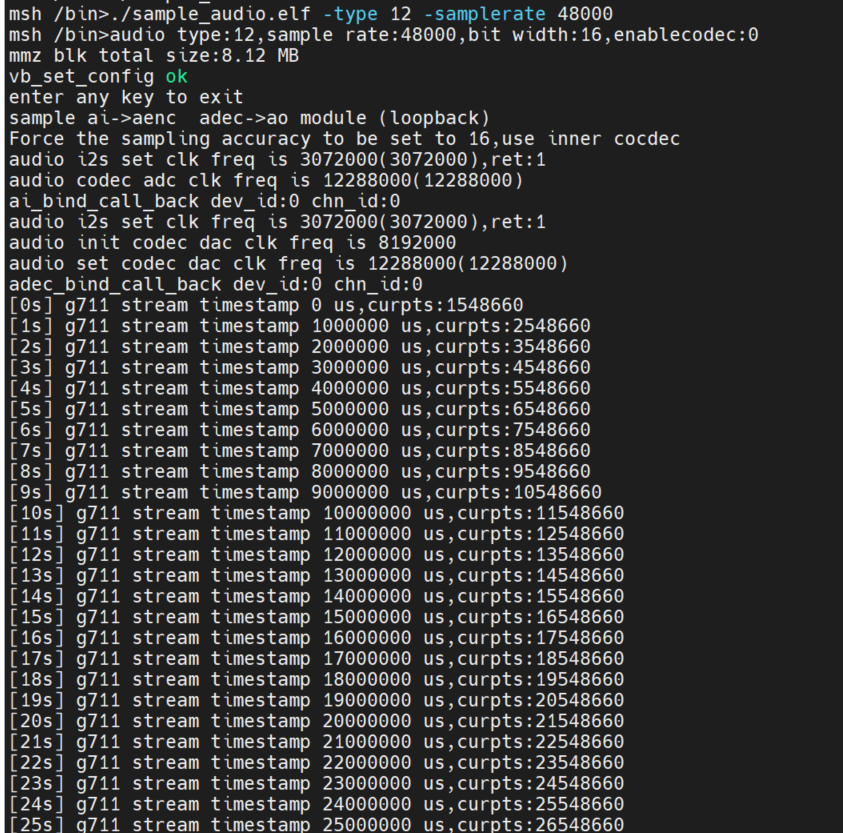
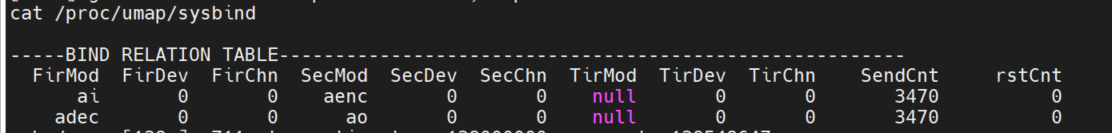
Entercat /proc/umap/sysbind to view the inter-module system bindings.
2.5.3.2.8 MAPI Audio Test#
Make sure that the intercore communication process is started: first confirm that the little core loads the k_ipcm.ko module, and then confirm that the big core starts:/sharefs/app/sample_sys_init.elf &
You can enter
/mnt/sample_audio -helphow to view the demo.-typeoption to test different module functionality.-samplerateoption to configure audio input and output with different sample rates (8K-192K), default is 44.1K.-enablecodecUse the built-in codec or off-chip audio daughter board, and use the built-in codec by default.-filenameLoad or store the G711 file name.-channels: Specifies the number of channels. 8
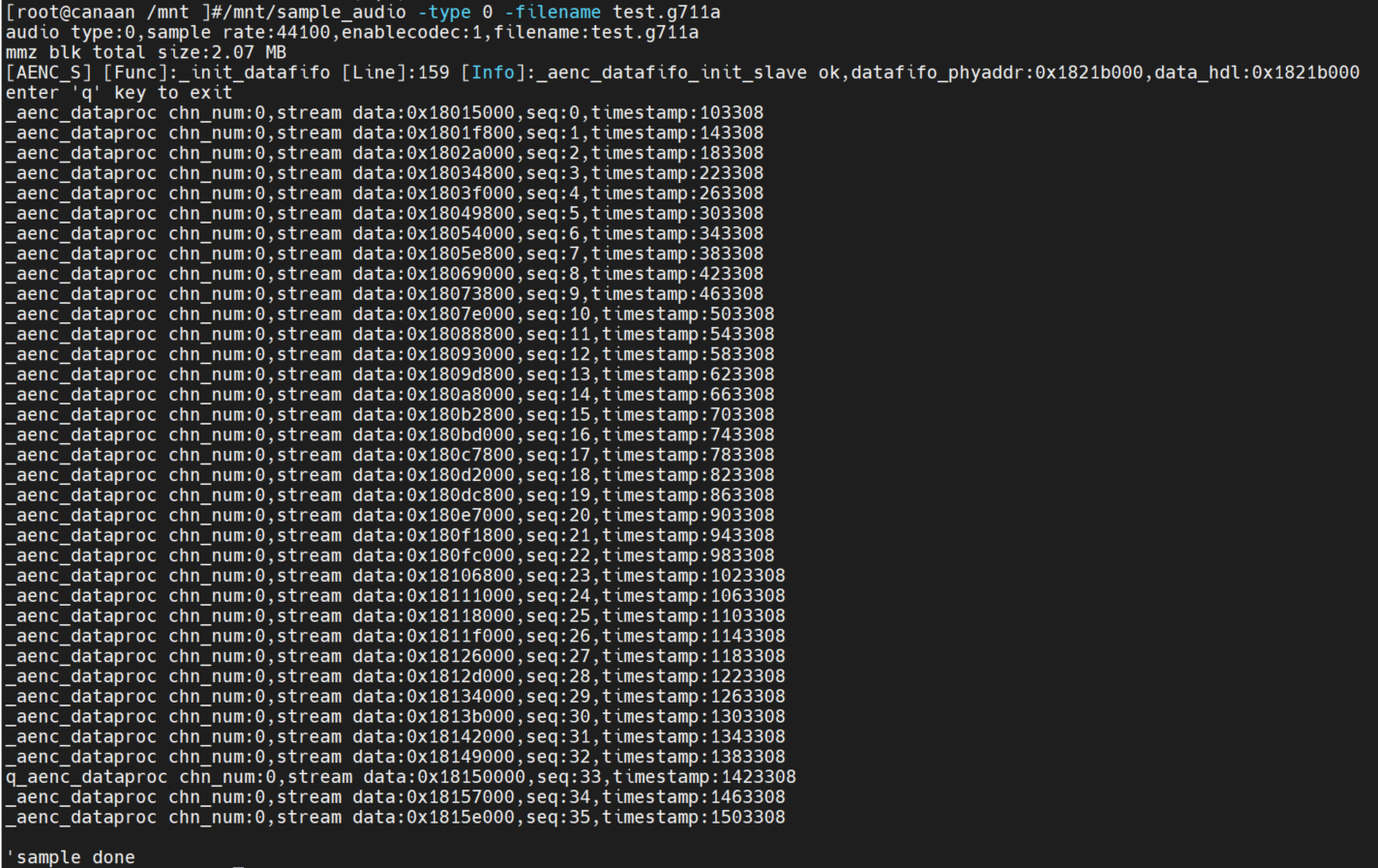
AI->AENC test
Execute command on the little core: /mnt/sample_audio -type 0 -filename test.g711aPress the q key to exit the test. The demo captures audio data in real time and encodes it into G711A format and saves it to a file.
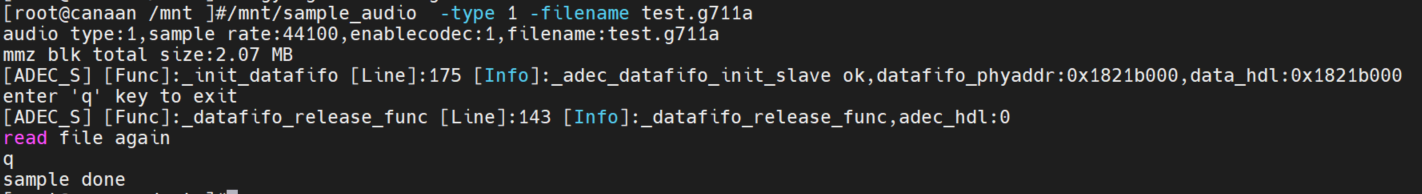
ADEC->AO test
Execute command on the little core: /mnt/sample_audio -type 1 -filename tes.g711aPress the q key to exit the test. The demo can loop decoding and play files in the local G711A format.
AI->aenc adec->ao loopback test
Run the command on the little core: /mnt/sample_audio -type 2 , press the q key to exit the test. The demo can collect audio data in real time and encode it into G711A format, and then decode the G711A format data and play the output.
2.6 Vicap_demo#
2.6.1 Introduction to vicap_demo#
VICAP Demo implements the camera data acquisition preview function by calling the MPI interface.
2.6.2 Feature description#
The CanMV development board uses the OV5647 camera module by default, which supports up to three data streams for a single camera.
2.6.3 Dependent Resources#
Camera module
2.6.4 Instructions for Use#
2.6.4.1 Compilation#
For a detailed description of the software compilation environment, refer to the SDKREADME.md.
Executed in the k230_sdk directory, the
make mpp-clean && rt-smart && make build-imagemodification of the big core is compiled into the SD card image, and the imagek230_sdk/output/k230_evb_defconfig/images/file will be generated under the directorysysimage-sdcard.img.
2.6.4.2 Execution#
Copy the
src/big/mpp/userapps/sample/elf/sample_vicap.elffile to the directory specified locallyMount this directory to the little core Linux via nfs
/sharefsOn the large kernel end, enter via
cd /sharefsthe command/sharefsExecute commands in this directory
./sample_vicapto obtain command help information
When you enter the : sample_vicapcommand, print the following prompt:
usage: ./sample_vicap -mode 0 -dev 0 -sensor 0 -chn 0 -chn 1 -ow 640 -oh 480 -preview 1 -rotation 1
Options:
-mode: vicap work mode[0: online mode, 1: offline mode. only offline mode support multiple sensor input] default 0
-dev: vicap device id[0,1,2] default 0
-dw: enable dewarp[0,1] default 0
-sensor: sensor type[0: ov9732@1280x720, 1: ov9286_ir@1280x720], 2: ov9286_speckle@1280x720]
-ae: ae status[0: disable AE, 1: enable AE] default enable
-awb: awb status[0: disable AWB, 1: enable AWb] default enable
-chn: vicap output channel id[0,1,2] default 0
-ow: the output image width, default same with input width
-oh: the output image height, default same with input height
-ox: the output image start position of x
-oy: the output image start position of y
-crop: crop enable[0: disable, 1: enable]
-ofmt: the output pixel format[0: yuv, 1: rgb888, 2: rgb888p, 3: raw], only channel 0 support raw data, default yuv
-preview: the output preview enable[0: disable, 1: enable], only support 2 output channel preview
-rotation: display rotaion[0: degree 0, 1: degree 90, 2: degree 270, 3: degree 180, 4: unsupport rotaion]
-help: print this help
The parameters are described as follows:
Parameter name |
Optional parameter value |
Parameter description |
|---|---|---|
-Dev |
0: vicap device 0 1: vicap device 1 2: vicap device 2. |
Specify the currently used vicap device, and the system supports up to three vicap devices. By specifying the device number, the binding relationship between the sensor and different vicap devices is realized. For example: -dev 1 -sensor 0 binds the ov9732 1280x720 RGB image output to vicap device 1. |
-mode |
0: Online mode; 1: Offline mode |
Specify the vicap device working mode, current before online mode and offline mode. For multiple sensor inputs, it must be specified as offline mode. |
-sensor |
23: OV5647 (CanMV development board only supports this sensor) |
Specifies the type of sensor currently in use |
-Chn |
0: vicap device output channel 0 1: vicap device output channel 1 2: vicap device output channel 2. |
Specify the output channel of the currently used vicap device, one vicap device supports up to three outputs, and only channel 0 supports RAW image format output |
-ow |
Specifies the output image width, which defaults to the input image width. The width needs to be 16 bytes aligned. If the default width exceeds the maximum width of the display output, the display output width is used as the final output width of the image If the output width is smaller than the input image width and the ox or oy parameters are not specified, the default is the scaled output |
|
-oh |
Specifies the output image height, which defaults to the input image height. If the default height exceeds the maximum height of the display output, the display output height is used as the final output height of the image If the output height is less than the input image height and the ox or oy parameter is not specified, the default is the scaled output |
|
-ox |
Specifies the horizontal start position of the image output, this parameter greater than 0 will perform the output cropping operation |
|
-Limited liability company |
Specifies the vertical start position of the image output, this parameter greater than 0 will perform the output cropping operation |
|
-crop |
0: Disable the cropping function 1: Enable the cropping function |
When the output image size is smaller than the input image size, the output is not scaled by default, or clipped if the flag is specified |
-ofmt |
0:YUV format output 1:RGB format output 2:RAW format output |
Specify the output image format, the default is YUV output. |
-preview |
0: Disable preview display 1: Enable preview display |
Specifies the output image preview display function. The default is enabled. Currently, up to 2 output images can be previewed at the same time. |
-rotation |
0: Rotate 0 degrees 1: Rotate 90 degrees 2: Rotate 180 degrees 3: Rotate 270 degrees 4: Rotation is not supported |
Specifies the rotation angle of the preview display window. By default, only the first output image window supports the rotation function. |
Example 1:
./sample_vicap -dev 0 -sensor 23 -chn 0 -chn 1 -ow 640 -oh 480
Note: Bind the ov5647@1920x1080 RGB output to vicap device 0 and enable vicap device output channel 0 and channel 1, where channel 0 output size defaults to the input image size (1920x1080) and channel 1 output image size is 640x480
2.7 DMA_demo#
2.7.1 Introduction to DMA_demo#
2.7.1.1 Unbound mode#
DMA channels 0-3 are GDMA and 4-7 are SDMA.
Channel 0 continuous input image with 1920x1080 resolution, 8bit, YUV400, single channel mode, output after rotation 90 degrees, and golden data comparison
Channel 1 continuous input image with 1280x720 resolution, 8bit, YUV420, dual-channel mode, output after rotation 180 degrees, and golden data comparison
Channel 2 continuous input image with resolution of 1280x720, 10bit, YUV420, triple channel mode, x-mirror, y-mirror post output, and golden data comparison
Channel 4 loops a piece of data in 1D mode, and compares it with the golden data after the transfer is completed
Channel 5 loops a piece of data in 2D mode, and compares it with the golden data after the transfer is completed
2.7.1.2 Binding mode#
Using VVI as the DMA analog input, channel 0 of VVI device 0 is bound to channel 0 of DMA, and channel 1 of VVI device 0 is bound to channel 1 of DMA. Every other second, vvi enters an image of 640x320, YUV400, 8bit, rotated 90°, and 640x320, YUV400, 8bit, rotated 180° to channel 1.
2.7.2 Feature description#
Including DMA device property configuration, channel property configuration, graphics input, output, release, pipeline binding and other functions.
2.7.3 Dependent Resources#
not
2.7.4 Instructions for Use#
2.7.4.1 Compilation#
Software compilation refers to the README.md in the release SDK package.
2.7.4.2 Execution#
Unbound mode demo runs
/sharefs/app/sample_dma.elf
A test message will be displayed on the screen, enter q to finish the run.
The bound mode demo runs
/sharefs/app/sample_dma_bind.elf
A test message will be displayed on the screen, enter q to finish the run.
2.8 USB_demo#
2.8.1 Introduction to USB_demo#
USB demo currently debugs 4 functions,
As a device, simulate a U disk, simulate a mouse and keyboard.
As host, connect a USB flash drive and connect a mouse and keyboard.
2.8.2 Feature description#
The functionality of the USB demo is the original integration of Linux systems.
2.8.3 Dependent Resources#
typeC line, typeC to typeA.
2.8.4 Instructions for Use#
2.8.4.1 Simulate a USB flash drive as a device#
#Plan a memory space as disk space to simulate a USB flash drive.
[root@canaan / ]#gadget-storage-mem.sh
2+0 records in
2+0 records out
mkfs.fat 4.1 (2017-01-24)
[ 1218.882053] Mass Storage Function, version: 2009/09/11
[ 1218.887308] LUN: removable file: (no medium)
[ 1218.895464] dwc2 91500000.usb-otg: bound driver configfs-gadget
[root@canaan / ]#[ 1219.019554] dwc2 91500000.usb-otg: new device is high-speed
[ 1219.056629] dwc2 91500000.usb-otg: new address 5
#Use the FAT partition of SD/eMMC as disk space to simulate a USB flash drive.
[root@canaan ~ ]#gadget-storage.sh
[ 359.995510] Mass Storage Function, version: 2009/09/11
[ 360.000762] LUN: removable file: (no medium)
[ 360.013138] dwc2 91500000.usb-otg: bound driver configfs-gadget
[root@canaan ~ ]#[ 360.136809] dwc2 91500000.usb-otg: new device is high-speed
[ 360.173543] dwc2 91500000.usb-otg: new address 43
Connect the USB port of the development board, connect typeC to the PC, and display the U disk connection on the PC.
2.8.4.2 Connect the USB flash drive as HOST#
The USB port of the K230 development board is connected to the U disk through typeC to typeA.
2.8.4.3 Simulate a mouse and keyboard as a device#
The K230 development board USB port is connected to another computer device through typeC for testing
[root@canaan / ]#gadget-hid.sh
[root@canaan / ]#hid_gadget_test /dev/hidg0 mouse
#Enter the corresponding operations according to the prompts, such as -123 -123, and you can see the mouse pointer on the PC move.
[root@canaan / ]#hid_gadget_test /dev/hidg1 keyboard
#Enter the corresponding operations according to the prompts, and you can see similar keyboard input on the PC. For example a b c --return
2.8.4.4 Connect a mouse and keyboard as HOST#
K230 development board USB connects mouse or keyboard via typeC to typeA.
#Use the following command to determine the event corresponding to the input device.
[root@canaan ~ ]#cat /proc/bus/input/devices
...
I: Bus=0003 Vendor=046d Product=c52f Version=0111
N: Name="Logitech USB Receiver"
P: Phys=usb-91500000.usb-otg-1/input0
S: Sysfs=/devices/platform/soc/91500000.usb-otg/usb1/1-1/1-1:1.0/0003:046D:C52F.0001/input/input2
U: Uniq=
H: Handlers=event2
B: PROP=0
B: EV=17
B: KEY=ffff0000 0 0 0 0
B: REL=1943
B: MSC=10
[root@canaan / ]$ test_mouse /dev/input/event2
#Click or move the mouse, and the serial port will display the corresponding display.
[root@canaan / ]$ test_keyboard /dev/input/event2
#Press different keys on the keyboard, and the serial port will have corresponding displays.
2.9 GPU_demo#
2.9.1 Introduction to GPU_demo#
The GPU demo contains a total of three executable programs
tiger: Example of drawing a vector drawing of a tigerlinearGrad: Draw a linear gradient exampleimgIndex: Draw a color lookup table
2.9.2 Feature description#
GPU demo mainly covers the three functions of GPU vector drawing, linear gradient (achieved through pattern), and color lookup table.
2.9.3 Dependent Resources#
The file system is writable.
2.9.4 Instructions for Use#
Go to a writable directory and execute the program
2.9.4.1 tiger#
Run the tigercommand and generate a tiger .png in the current directory after execution, as shown in the following figure

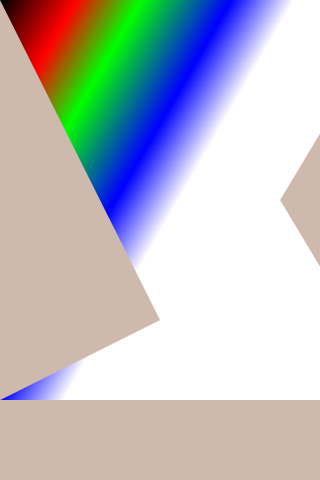
2.9.4.2 linear degrees#
Run the linearGradcommand and generate a linearGrad .png in the current directory after execution, as shown in the following figure
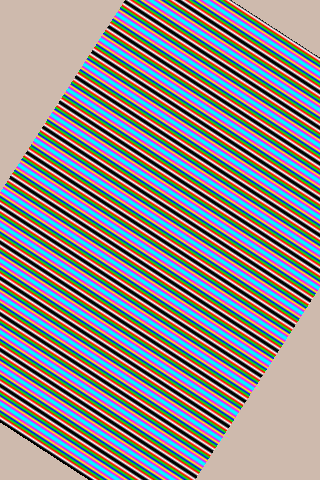
2.9.4.3 imgIndex#
Run the imgIndexcommand and generate four image files in the current directory, as shown in the following figure
imgIndex1.png: index1 mode, supports 2 colors

imgIndex2.png: index2 mode, supports 4 colors

imgIndex4.png: index4 mode, supports 16 colors

imgIndex8.png: index8 mode, supports 256 colors
2.9.4.4 vglite_drm#
Run the vglite_drmcommand, which displays the pattern drawn by the GPU on the LCD screen, and pressEnter the key again to display the next pattern, as shown in the figure

2.9.4.5 vglite_cube#
Run the vglite_cubecommand and a rotating cube drawn by the GPU will be displayed on the LCD screen, as shown in the following figure

This demo runtime kernel will have a large number of print messages, if you do not want these messages to be displayed, you can reduce the kernel print level
sysctl -w kernel.printk=6
2.10 DRM display demo#
2.10.1 Introduction to using demo#
The demo runs on a K230 small-core Linux system and displays the image on the screen.
2.10.2 Features Description#
DRM supports 5 layer operations, including: 1 video layer and 4 OSD layers;
The video layer supports NV12, NV21, NV16, NV61 color spaces
The OSD layer supports ARGB8888, ARGB4444, RGB888, RGB565 color spaces
2.10.3 Dependent Resources#
HDMI monitor
2.10.4 Instructions for Use#
2.10.4.1 Compilation#
Software compilation refers to the README.md in the release SDK package
2.10.4.2 Execution#
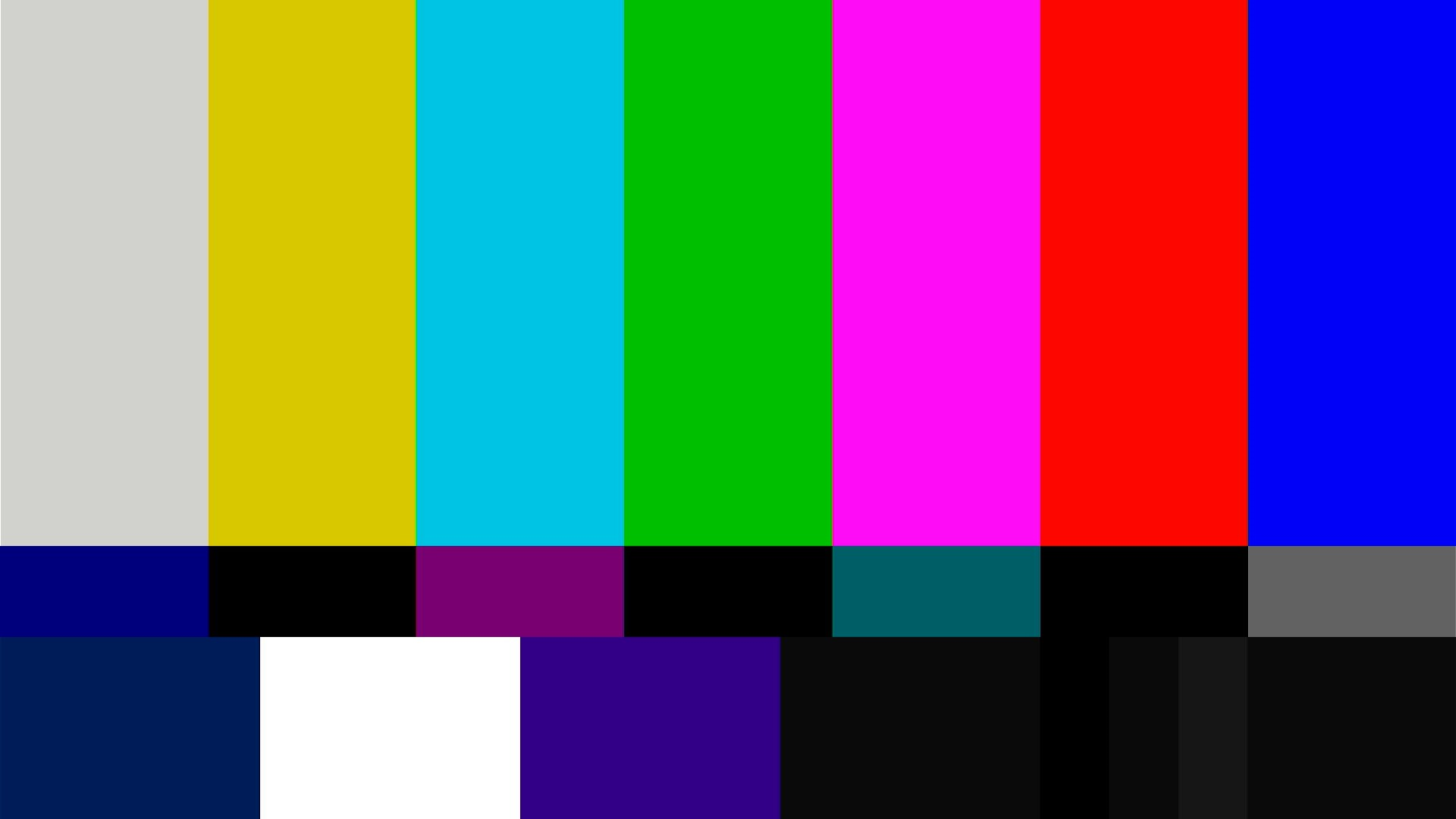
modetest -M canaan-drm -D 0 -a -s 38@36:1920x1080-30 -P 32@36:1920x1080@AR24 -v -F smpte
After executing the above command, a color bar will be displayed on the HDMI monitor, as follows:

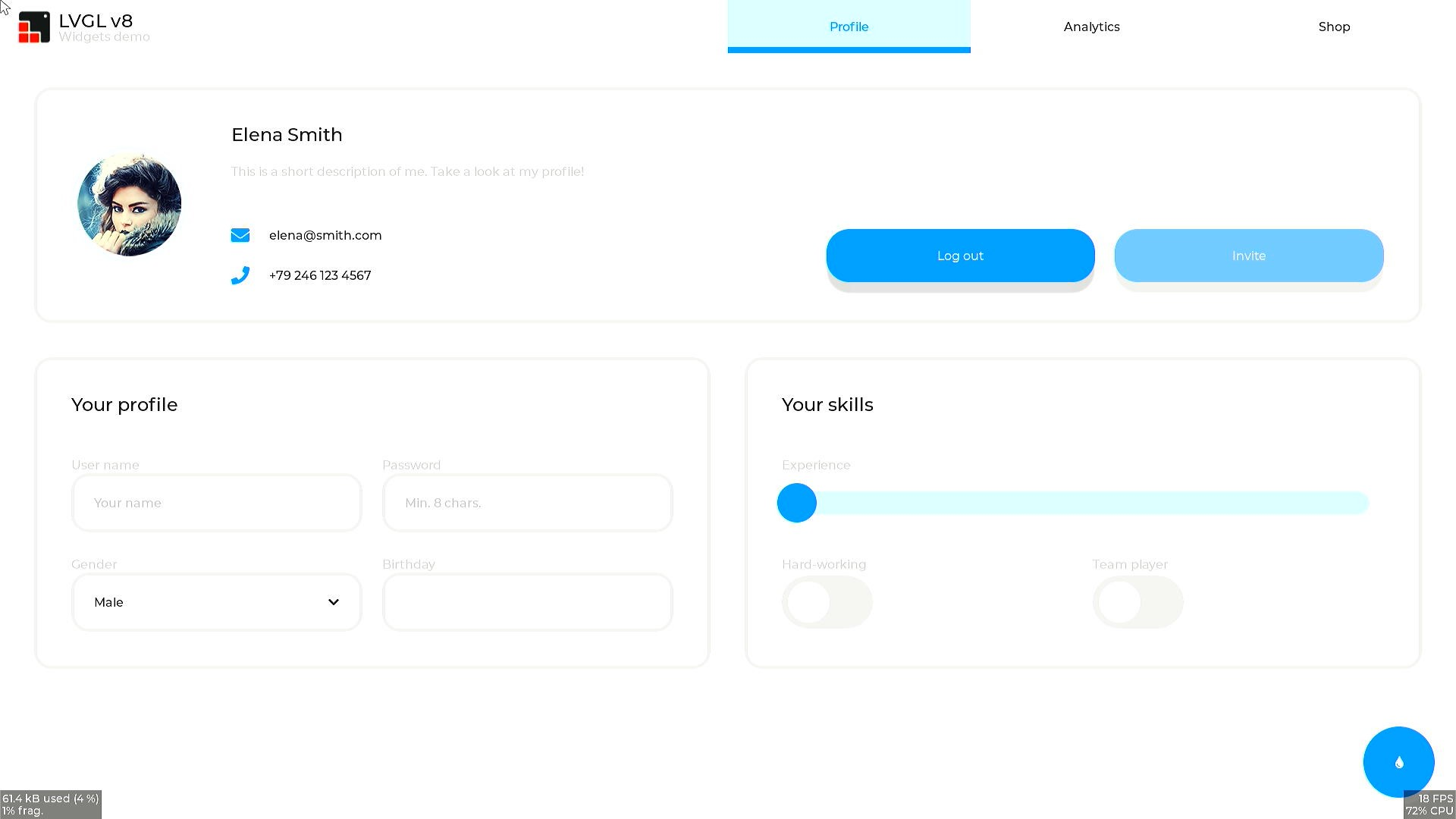
2.11 LVGL demo#
2.11.1 Introduction to using demo#
The demo runs on a K230 small-core Linux system and displays a configuration interface on an HDMI display.
2.11.3 Dependent Resources#
HDMI monitor
2.11.3 Instructions for Use#
2.11.3.1 Compilation#
Software compilation refers to the README.md in the release SDK package
2.11.3.2 Execution#
lvgl_demo_widgets
After executing the above command, the configuration interface will be displayed on the HDMI monitor, as follows:
2.14 Rtsp push streaming Demo#
2.12.1 Introduction to Demo#
This demo implements RTSP streaming.
2.12.2 Feature description#
The demo supports simultaneous push of audio and video streams to RTSP Server, which mapi venc&aencencodes audio and video through interfaces; after pushing, the demo supports three URL push and pull streams.
2.12.3 Dependent Resources#
A USB-to-ETH network port converter is required, and the development board is connected to the network cable
2.12.4 Instructions for Use#
2.12.4.1 Compilation#
Refer to the introduction in the Release SDK packageREADME.md, you can compile cdk-user in the docker environment, andk230_sdk/src/common/cdk/user/out/little generate the executable program rtsp_demo after the compilation is completed
2.12.4.2 Execution#
rtsp_demo the sensor type used by default is IMX335_MIPI_2LANE_RAW12_1920X1080_30FPS_LINEAR, the sensor type and other parameters can be modified by passing parameters from the command line, as follows:
After launching the board:
Use
lsmodto check whether the k_ipcm module is loaded on the little core side. If it is not loaded, executeinsmod k_ipcm.koto load the k_ipcm module.Start the internuclear communication process on the large nuclear side, execute
./sample_sys_inif.elfIn the little core side/mnt directory, execute, the
./rtsp_demodefault is 1-channel H265 video encoding push, the resolution is 1280x720, if you need to refer to the following parameter description, when pushing the MJPEG code stream, the resolution currently supports a maximum of 2032x1944, and the minimum resolution is 640x480
Usage: ./rtsp_demo -s 0 -n 2 -t h265 -w 1280 -h 720 -a 0
-s: the sensor type:
see vicap doc
-n: the session number, range: 1, 2,3
-t: the video encoder type: h264/h265/mjpeg
-w: the video encoder width
-h: the video encoder height
-a: audio input type(0:mic input 1:headphone input):default 0.
The sensor type value is described in the k230_docs/en/01_software/board/mpp/K230_Camera_Sensor_Adaptation_Guide.mdk_vicap_sensor_type in the document
Audio input type selectable: onboard MIC or headphone input.
After the rtsp_demo on the little core runs normally, the URL address of the form will be printed, rtsp://ip:8554/session0 where 0 represents the 0th way, which can be played through the stream of VLC pulling URLs; if you need to stop running, please stop VLC pulling the stream first, and then execute thectrl+c Stop Running rtsp_demo.
2.13 FaceAe Demo#
2.13.1 Demo introduction#
This demo is used in the big core, which is a demo of VICAP, KPU, VO (video output), and AERoi joint debugging, and can appropriately adjust the face exposure brightness through the face detection interface.
2.13.2 Compilation#
First refer to the README.md in the release SDK package and compile the image using Docker.
After the compilation is complete, the sample (sample_face_ae.elf) is stored in this path by default
k230_sdk/src/big/mpp/userapps/sample/elfSince KPU linkage requires the use of the detection model test.kmodel, the path is stored after compilation
k230_sdk/src/big/mpp/userapps/sample/elf
2.13.3 Execution#
cd /sharefs/app
./sample_face_ae.elf test.kmodel 1 # arg1: Model name, arg2: enable face ae
Wait for the initialization to complete and prompt any letter + enter,
for example:Type a, press Enter, and run face ae demo
After successful execution, the physical address of each frame of image will be printed.
2.14 FFT Demo#
2.14.1 Introduction to Demo#
This demo is used to verify the use of FFT APIs and test FFT functions, see src/big/mpp/userapps/sample/sample_fft/
2.14.2 Feature description#
First, the FFT calculation is performed, and the IFT calculation is performed
2.14.3 Dependent Resources#
not
2.14.4 Instructions for Use#
2.14.4.1 Compilation#
Please refer to the README.md in the release SDK package.
2.14.4.2 Execution#
After the large and little core systems are up, execute the following command on the big core command line:
cd /sharefs/app;./sample_fft.elf
The output content of the big core serial port is as follows:
msh /sharefs/app>./sample_fft.elf 1 0 -----fft ifft point 0064 ------- max diff 0003 0001 i=0045 real hf 0000 hif fc24 org fc21 dif 0003 i=0003 imag hf ffff hif 0001 org 0000 dif 0001 -----fft ifft point 0064 use 133 us result: ok -----fft ifft point 0128 ------- max diff 0003 0002 i=0015 real hf 0001 hif fca1 org fc9e dif 0003 i=0031 imag hf 0001 hif fffe org 0000 dif 0002 -----fft ifft point 0128 use 121 us result: ok -----fft ifft point 0256 ------- max diff 0003 0001 i=0030 real hf 0000 hif fca1 org fc9e dif 0003 i=0007 imag hf ffff hif 0001 org 0000 dif 0001 -----fft ifft point 0256 use 148 us result: ok -----fft ifft point 0512 ------- max diff 0003 0003 i=0060 real hf 0000 hif fca1 org fc9e dif 0003 i=0314 imag hf 0001 hif fffd org 0000 dif 0003 -----fft ifft point 0512 use 206 us result: ok -----fft ifft point 1024 ------- max diff 0005 0002 i=0511 real hf 0000 hif fc00 org fc05 dif 0005 i=0150 imag hf 0000 hif fffe org 0000 dif 0002 -----fft ifft point 1024 use 328 us result: ok -----fft ifft point 2048 ------- max diff 0005 0003 i=1022 real hf 0000 hif fc00 org fc05 dif 0005 i=1021 imag hf 0000 hif 0003 org 0000 dif 0003 -----fft ifft point 2048 use 574 us result: ok -----fft ifft point 4096 ------- max diff 0005 0002 i=4094 real hf 027b hif 041f org 0424 dif 0005 i=0122 imag hf 0000 hif 0002 org 0000 dif 0002 -----fft ifft point 4096 use 1099 us result: ok
2.15 SDIO WIFI#
2.15.1 Introduction to Demo#
The CANMV development board uses a SDIO WIFI that supports 2.4G, AP6212. Supports STA and softAP modes.
2.15.2 Compilation#
The configuration of k230_sdk compiled CANMV supports AP6212 WIFI by default.
make menuconfig
K230 SDK Configuration
wifi configurations --->
[*] enable ap6212a
After enabling ap6212a, k230_sdk will copy the firmware and nvram.txt required by WIFI to rootfs.
make linux-menuconfig
Linux/riscv 5.10.4 Kernel Configuration
Device Drivers --->
[*] Network device support --->
[*] Wireless LAN --->
<M> Broadcom FullMAC wireless cards support
(/etc/firmware/fw_bcm43456c5_ag.bin) Firmware path
(/etc/firmware/nvram.txt) NVRAM path
Enable Chip Interface (SDIO bus interface support) --->
Interrupt type (In-Band Interrupt) --->
Configure LINUX to compile the WIFI driver. CANMV WIFI defaults to the STA and SoftAP concurrent mode. Source code path:
src/little/linux/drivers/net/wireless/bcmdhd
make buildroot-menuconfig
Buildroot 2021.02-git Configuration
Target packages --->
Networking applications --->
[*] hostapd
[*] Enable hostap driver
[*] Enable nl80211 driver
[ ] Enable wired driver
[*] Enable ACS
[*] Enable EAP
[*] Enable WPS
[*] Enable WPA3 support
[*] Enable VLAN support
[*] Enable dynamic VLAN support
[*] Use netlink-based API for VLAN operations
[*] wireless tools
[*] Install shared library
[*] wpa_supplicant
[*] Enable nl80211 support
[*] Enable AP mode
[*] Enable Wi-Fi Display
[*] Enable mesh networking
[*] Enable autoscan
[*] Enable EAP
[*] Enable HS20
[*] Enable syslog support
[*] Enable WPS
[*] Enable WPA3 support
[*] Install wpa_clibinary
[ ] Install wpa_client shared library
[*] Install wpa_passphrase binary
[*] Enable support for the DBus control interface
Compile buildroot and add tools for wireless use.
The WIFI module is reset in uboot when the system starts. Source code:
src/little/uboot/board/canaan/k230_canmv/board.c : board_late_init
After the WIFI module is started in the system, power on and off the WIFI module if wlan down/up. Source code:
&gpio1 {
status = "okay";
};
&mmc_sd0{
status = "okay";
io_fixed_1v8;
rx_delay_line = <0x00>;
tx_delay_line = <0x00>;
bcmdhd_wlan {
compatible = "android,bcmdhd_wlan";
gpio_wl_reg_on = <&port1 0 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>;
};
};
2.15.3 Execution#
STA is the abbreviation of Station. It is a terminal site device in the wireless network and can be regarded as a client. Generally speaking, the device in STA mode itself does not accept wireless access. The device is connected to the AP node. For network access, our mobile phone acts as an STA to connect to the router.
AP is the abbreviation of Access Point, which is a wireless access point. It is the central node of a wireless network and can be regarded as a server. As the central node of a network, it provides wireless access services. Other wireless devices are allowed to access the node. All wireless signal data of devices accessing the node must pass through it for exchange and mutual access. General wireless routers, gateways, and hotspots work in AP mode, and AP nodes are allowed to connect to each other.
2.15.3.1 STA test#
ifconfig -a
ifconfig wlan0 up
wpa_supplicant -D nl80211 -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf -B
wpa_cli -i wlan0 scan
wpa_cli -i wlan0 scan_result
wpa_cli -i wlan0 add_network
wpa_cli -i wlan0 set_network 1 psk '"12345678"'
wpa_cli -i wlan0 set_network 1 ssid '"wifi_test"'
wpa_cli -i wlan0 select_network 1
udhcpc -i wlan0 -q
2.15.3.2 AP test#
[root@canaan ~ ]#cat /etc/hostapd.conf
ctrl_interface=/var/run/hostapd
driver=nl80211
ieee80211n=1
interface=wlan1
hw_mode=g
channel=6
beacon_int=100
dtim_period=1
ssid=k230_ap
auth_algs=1
ap_isolate=0
ignore_broadcast_ssid=0
ifconfig wlan1 192.168.1.1
udhcpd /etc/udhcpd.conf &
hostapd /etc/hostapd.conf &
sta can directly connect to the passwordless “k230_ap” hotspot.