K230 Inter-Core Communication API Reference#
Preface#
Overview#
This document mainly introduces the functions and usage of the system control module in the media subsystem. The functions and usage of other modules will be discussed in their respective documents.
Target Audience#
This document (this guide) is mainly applicable to the following personnel:
Technical Support Engineers
Software Development Engineers
Abbreviation Definitions#
Abbreviation |
Description |
|---|---|
ipcm |
internal processor communication module |
IPCMSG |
internal processor communication message |
Revision History#
Document Version |
Modification Description |
Modifier |
Date |
|---|---|---|---|
v1.0 |
Initial version |
Haibo Hao |
2023/3/8 |
1. Overview#
1.1 Overview#
This document describes the relevant content of K230 heterogeneous inter-core communication.
1.1.1 Inter-Core Communication Implementation Principle#
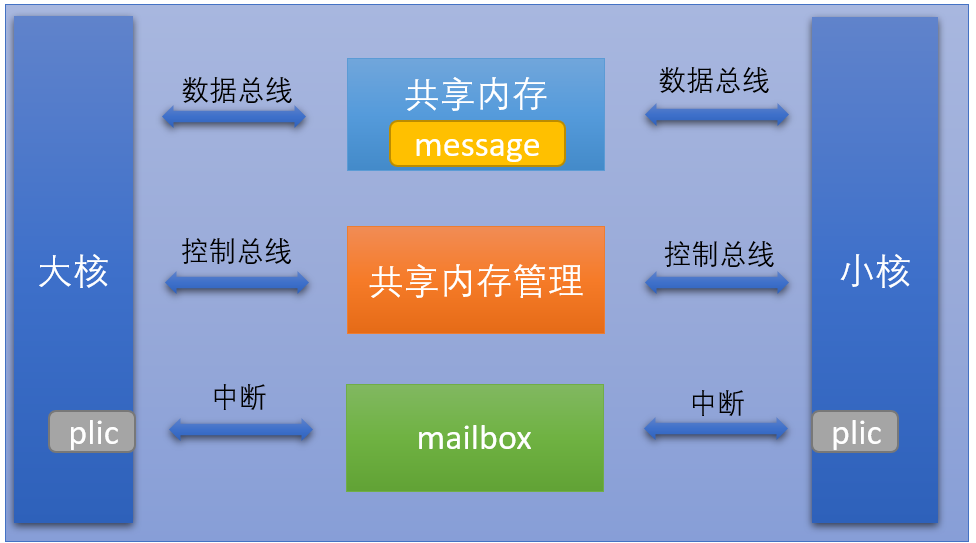
Shared memory is used for the specific content of communication messages sent by large and small cores.
Shared memory management is used to identify the attributes of communication messages such as address, size, port number, etc.
Mailbox realizes the notification mechanism after large and small cores send messages through interrupts.
1.1.2 Memory Space Usage#
Currently, the data shared memory area used by large and small cores is designed with a total space of 1M, with each party involved in the communication occupying 512KB for sending and receiving. The shared memory area used to maintain the state of each core is 4KB.
1.2 Function Description#
1.2.1 IPCMSG#
IPCMSG is a component for communication between large and small cores of K230 in user mode, mainly used for sending control messages. This module includes functions such as adding and deleting services, creating and deleting messages, disconnecting, and sending messages. It supports three types of message sending: sending asynchronous messages, sending synchronous messages, and sending messages that do not require a reply from the other party. Among them, synchronous messages support a timeout mechanism, and users can set the timeout period when calling the API. For messages that need a reply, if the reply is received after 60 seconds, the reply message will be discarded.
1.2.2 DATAFIFO#
DATAFIFO is a component used for inter-core communication when large and small cores of K230 perform large data interactions (such as encoded data) in user mode. Internally, it mainly uses shared memory to complete data interaction, transmitting data pointers without copying the data content. The notification of data sending and receiving relies on thread polling.
DATAFIFO mainly includes opening and closing channels, writing and reading data, and other control commands.
2. API Reference#
2.1 IPCMSG#
This functional module provides the following APIs:
2.1.1 kd_ipcmsg_add_service#
[Description]
Add a service
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_ipcmsg_add_service(const k_char* pszServiceName, const k_ipcmsg_connect_s* pstConnectAttr);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
pszServiceName |
Pointer to the service name. |
Input |
pstConnectAttr |
Attribute structure of the connection to the server. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
Multiple services can be added, but different services cannot use the same port number. Clients and services communicate through the same port number, so one service corresponds to one client.
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.2 kd_ipcmsg_del_service#
[Description]
Delete a service
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_ipcmsg_del_service(const k_char* pszServiceName);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
pszServiceName |
Pointer to the service name. Maximum length: K_IPCMSG_MAX_SERVICENAME_LEN. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.3 kd_ipcmsg_try_connect#
[Description]
Establish a connection in a non-blocking manner
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_ipcmsg_try_connect(k_s32* ps32Id, const k_char* pszServiceName, k_ipcmsg_handle_fn_ptr pfnMessageHandle);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
ps32Id |
Pointer to the message communication ID. |
Output |
pszServiceName |
Pointer to the service name. |
Input |
pfnMessageHandle |
Callback function for message handling. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.4 kd_ipcmsg_connect#
[Description]
Establish a connection in a blocking manner
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_ipcmsg_connect(k_s32* ps32Id, const k_char* pszServiceName, k_ipcmsg_handle_fn_ptr pfnMessageHandle);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
ps32Id |
Pointer to the message communication ID. |
Output |
pszServiceName |
Pointer to the service name. |
Input |
pfnMessageHandle |
Message handling function. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.5 kd_ipcmsg_disconnect#
[Description]
Disconnect
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_ipcmsg_disconnect(k_s32 s32Id);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
s32Id |
Message communication ID. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.6 kd_ipcmsg_is_connect#
[Description]
Check if the message communication is connected.
[Syntax]
k_bool kd_ipcmsg_is_connect(k_s32 s32Id);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
s32Id |
Message communication ID. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
K_TRUE |
Connected. |
K_FALSE |
Not connected. |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.7 kd_ipcmsg_send_only#
[Description]
Only send a message to the other end without receiving a return value from the other end.
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_ipcmsg_send_only(k_s32 s32Id, k_ipcmsg_message_s *pstRequest);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
s32Id |
Message service ID. |
Input |
pstRequest |
Pointer to the message structure. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.8 kd_ipcmsg_send_async#
[Description]
Send an asynchronous message. This interface is non-blocking; it returns after sending the message to the other end without waiting for the message command to be processed.
If this interface is used to send a reply message, no reply from the other end is required; otherwise, the other end must reply.
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_ipcmsg_send_async(k_s32 s32Id, k_ipcmsg_message_s* pstMsg, k_ipcmsg_resphandle_fn_ptr pfnRespHandle);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
s32Id |
Message service ID. |
Input |
pstMsg |
Pointer to the message. |
Input |
pfnRespHandle |
Message reply handling function. When sending a reply message, it can be NULL; otherwise, it must not be NULL. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.9 kd_ipcmsg_send_sync#
[Description]
Send a synchronous message. This interface will block and wait until the message command from the other end is processed before returning.
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_ipcmsg_send_sync(k_s32 s32Id, k_ipcmsg_message_s* pstMsg, k_ipcmsg_message_s** ppstMsg, k_s32 s32TimeoutMs);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
s32Id |
Message service ID. |
Input |
pstMsg |
Pointer to the message. |
Input |
ppstMsg |
Pointer to the reply message. |
Output |
s32TimeoutMs |
Timeout period in milliseconds. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
In case of a timeout, this interface will internally call kd_ipcmsg_destroy_message to destroy *ppstMsg (reply message). Since the same message cannot be destroyed twice, there is no need to destroy the reply message again after the timeout exits.
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.10 kd_ipcmsg_run#
[Description]
Message processing function
[Syntax]
k_void kd_ipcmsg_run(k_s32 s32Id);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
s32Id |
Message service ID. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
void |
None |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.11 kd_ipcmsg_create_message#
[Description]
Create a message
[Syntax]
k_ipcmsg_message_s * kd_ipcmsg_create_message(k_u32 u32Module, k_u32 u32CMD, k_void* pBody, k_u32 u32BodyLen);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
u32Module |
Module ID, created by the user, used to distinguish different messages from different modules. |
Input |
u32CMD |
Command ID, created by the user, used to distinguish different commands within the same module. |
Input |
pBody |
Pointer to the message body. |
Input |
u32BodyLen |
Size of the message body. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
k_ipcmsg_message_s* |
Pointer to the message structure. |
null |
Message creation failed. |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.12 kd_ipcmsg_create_resp_message#
[Description]
Create a reply message
[Syntax]
k_ipcmsg_message_s* kd_ipcmsg_create_resp_message(k_ipcmsg_message_s* pstRequest, k_s32 s32RetVal, k_void* pBody, k_u32 u32BodyLen);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
pstRequest |
Pointer to the request message. |
Input |
s32RetVal |
Return value of the reply. |
Input |
pBody |
Pointer to the reply message body. |
Input |
u32BodyLen |
Size of the reply message body. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
k_ipcmsg_message_s* |
Pointer to the message structure. |
null |
Message creation failed. |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.1.13 kd_ipcmsg_destroy_message#
[Description]
Destroy a message
[Syntax]
k_void kd_ipcmsg_destroy_message(k_ipcmsg_message_s* pstMsg);
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
pstMsg |
Pointer to the message. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
k_void |
None |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_comm_ipcmsg.h k_ipcmsg.h
Library files: libipcmsg.a
[Notes]
The same message cannot be destroyed multiple times, otherwise it will cause system exceptions.
[Example]
None
[Related Topics]
2.2 DATAFIFO#
This functional module provides the following APIs:
2.2.1 kd_datafifo_open#
[Description]
Open a data channel.
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_datafifo_open(k_datafifo_handle* Handle, k_datafifo_params_s* pstParams)
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
Handle |
Data channel handle. |
Output |
pstParams |
Pointer to data channel parameters. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_datafifo.h
Library files: libdatafifo.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
2.2.2 kd_datafifo_open_by_addr#
[Description]
Open a data channel by physical address.
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_datafifo_open_by_addr(k_datafifo_handle *Handle, k_datafifo_params_s *pstParams, k_u64 u64Phyaddr)
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
Handle |
Data channel handle. |
Output |
pstParams |
Pointer to data channel parameters. |
Input |
u32PhyAddr |
Physical address of the data buffer. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_datafifo.h
Library files: libdatafifo.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
2.2.3 kd_datafifo_close#
[Description]
Close a data channel.
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_datafifo_close(k_datafifo_handle Handle)
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
Handle |
Data channel handle. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_datafifo.h
Library files: libdatafifo.a
[Notes]
When closing DataFifo, to ensure the normal release of data at both the read and write ends, the user needs to ensure that the read end reads all the data existing in DataFifo. After the write end finishes writing data, it needs to call kd_datafifo_write (Handle, NULL) once to trigger the release of data at the write end and update the read pointer.
[Example]
None
2.2.4 kd_datafifo_read#
[Description]
Read data.
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_datafifo_read(k_datafifo_handle Handle, void** ppData)
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
Handle |
Data channel handle. |
Input |
ppData |
Pointer to the data read. |
Output |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_datafifo.h
Library files: libdatafifo.a
[Notes]
None
[Example]
None
2.2.5 kd_datafifo_write#
[Description]
Write data.
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_datafifo_write(k_datafifo_handle Handle, void* pData)
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
Handle |
Data channel handle. |
Input |
pData |
Data to be written. |
Input |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_datafifo.h
Library files: libdatafifo.a
[Notes]
When pData is NULL, it triggers the data release callback function at the write end and updates the read tail pointer.
[Example]
None
2.2.6 kd_datafifo_cmd#
[Description]
Other operations.
[Syntax]
k_s32 kd_datafifo_cmd(k_datafifo_handle Handle, k_datafifo_cmd_e enCMD, void* pArg)
[Parameters]
Parameter Name |
Description |
Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
Handle |
Data channel handle. |
Input |
enCMD |
Operation command. |
Input |
pArg |
Parameter, see [Notes]. |
Input/Output |
[Return Value]
Return Value |
Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Success. |
Non-zero |
Failure, with the value being error code |
[Chip Differences]
None
[Requirements]
Header files: k_datafifo.h
Library files: libdatafifo.a
[Notes]
Control commands and corresponding parameters:
Command |
Parameter and Description |
|---|---|
DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_PHY_ADDR |
Returns the physical address of the DATAFIFO, k_u64 type. |
DATAFIFO_CMD_READ_DONE |
After the read end uses the data, it needs to call this to update the head and tail pointers of the read end. |
DATAFIFO_CMD_WRITE_DONE |
After the write end finishes writing data, it needs to call this to update the write end’s write pointer. No return value, parameter can be NULL. |
DATAFIFO_CMD_SET_DATA_RELEASE_CALLBACK |
Data release callback function. |
DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_AVAIL_WRITE_LEN |
Returns the number of data items that can be written, k_u32 type. Note: Since one data item is reserved for buffer management, the actual length available for buffering data is one data item length (u32CacheLineSize) less than the configured DATAFIFO length (u32EntriesNum * u32CacheLineSize). |
DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_AVAIL_READ_LEN |
Returns the number of data items that can be read, k_u32 type. |
[Example]
None
3. Data Types#
3.1 IPCMSG#
This module has the following data types:
3.1.1 K_IPCMSG_MAX_CONTENT_LEN#
[Description]
Defines the maximum length of the message body.
[Definition]
#define K_IPCMSG_MAX_CONTENT_LEN (1024)
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
None
This module has the following data types:
3.1.2 K_IPCMSG_PRIVDATA_NUM#
[Description]
Defines the maximum number of private data items in the message body.
[Definition]
#define K_IPCMSG_PRIVDATA_NUM (8)
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
None
3.1.3 K_IPCMSG_INVALID_MSGID#
[Description]
Defines an invalid message ID.
[Definition]
#define K_IPCMSG_INVALID_MSGID (0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF)
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
None
3.1.4 k_ipcmsg_connect_s#
[Description]
Defines the module ID enumeration type.
[Definition]
typedef struct IPCMSG_CONNECT_S
{
k_u32 u32RemoteId;
k_u32 u32Port;
k_u32 u32Priority;
} k_ipcmsg_connect_s;
[Members]
Member Name |
Description |
|---|---|
u32RemoteId |
Enumeration value indicating the remote CPU connection. 0: small core; 1: large core |
u32Port |
Custom port number for message communication. Range: [0, 512] |
u32Priority |
Priority of message delivery. Range: 0: normal priority; 1: high priority. Default is 0 |
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
3.1.5 k_ipcmsg_messsage_s#
[Description]
Defines the message structure.
[Definition]
typedef struct IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S
{
k_bool bIsResp; /**< Identify the response message */
k_u64 u64Id; /**< Message ID */
k_u32 u32Module; /**< Module ID, user-defined */
k_u32 u32CMD; /**< CMD ID, user-defined */
k_s32 s32RetVal; /**< Return Value in response message */
k_s32 as32PrivData[K_IPCMSG_PRIVDATA_NUM]; /**< Private data, can be modified directly after ::kd_ipcmsg_create_message or ::kd_ipcmsg_create_resp_message */
void* pBody; /**< Message body */
k_u32 u32BodyLen; /**< Length of pBody */
} k_ipcmsg_message_t;
[Members]
Member Name |
Description |
|---|---|
bIsResp |
Indicates whether the message is a response: K_TRUE: yes; K_FALSE: no |
u64Id |
Message ID |
u32Module |
Module ID |
u32CMD |
CMD ID |
s32RetVal |
Return value |
as32PrivData |
Private data |
pBody |
Pointer to the message body |
u32BodyLen |
Length of the message body in bytes |
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
3.1.6 k_ipcmsg_handle_fn_ptr#
[Description]
Defines the message response handling function.
[Definition]
typedef void (*k_ipcmsg_handle_fn_ptr)(k_s32 s32Id, k_ipcmsg_message_s* pstMsg);
[Members]
Member Name |
Description |
|---|---|
s32Id |
Message service ID |
pstMsg |
Pointer to the message body |
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
3.2 DATAFIFO#
This module has the following data structures:
3.2.1 k_datafifo_handle#
[Description]
Defines the DATAFIFO handle.
[Definition]
typedef K_U32 K_DATAFIFO_HANDLE;
[Members]
Member Name |
Description |
|---|---|
s32Id |
Message service ID |
pstMsg |
Pointer to the message body |
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
None
3.2.2 K_DATAFIFO_INVALID_HANDLE#
[Description]
Defines an invalid handle for the data channel.
[Definition]
#define K_DATAFIFO_INVALID_HANDLE (-1)
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
None
3.2.3 K_DATAFIFO_RELEASESTREAM_FN_PTR#
[Description]
Defines the data channel stream release function.
[Definition]
typedef void (*K_DATAFIFO_RELEASESTREAM_FN_PTR)(void* pStream);
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
None
3.2.4 K_DATAFIFO_OPEN_MODE_E#
[Description]
Defines the open mode of the data channel.
[Definition]
typedef struct k_DATAFIFO_PARAMS_S
{
k_u32 u32EntriesNum; /**< The number of items in the ring buffer */
k_u32 u32CacheLineSize; /**< Item size */
k_bool bDataReleaseByWriter; /**< Whether the data buffer release by writer */
K_DATAFIFO_OPEN_MODE_E enOpenMode; /**< READER or WRITER */
} k_datafifo_params_s;
[Members]
Member Name |
Description |
|---|---|
DATAFIFO_READER |
Reader role, only reads data |
DATAFIFO_WRITER |
Writer role, only writes data |
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
None
3.2.5 k_datafifo_params_s#
[Description]
Defines the configuration parameters for the data channel.
[Definition]
typedef struct k_DATAFIFO_PARAMS_S
{
k_u32 u32EntriesNum; /**< The number of items in the ring buffer */
k_u32 u32CacheLineSize; /**< Item size */
k_bool bDataReleaseByWriter; /**< Whether the data buffer release by writer */
K_DATAFIFO_OPEN_MODE_E enOpenMode; /**< READER or WRITER */
} k_datafifo_params_s;
[Members]
Member Name |
Description |
|---|---|
u32EntriesNum |
Number of items in the ring buffer |
u32CacheLineSize |
Size of each item |
bDataReleaseByWriter |
Whether the writer releases data |
enOpenMode |
Role of the open channel |
[Notes]
There are no restrictions on the values of u32EntriesNum and u32CacheLineSize. As long as the MMZ memory is large enough, DATAFIFO can be successfully created. Therefore, users need to ensure that these two parameters are within a reasonable range.
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
None
3.2.6 k_datafifo_cmd_e#
[Description]
Defines the control types for the data channel.
[Definition]
typedef enum k_DATAFIFO_CMD_E
{
DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_PHY_ADDR, /**< Get the physical address of the ring buffer */
DATAFIFO_CMD_READ_DONE, /**< When the read buffer is read over, the reader should call this function to notify the writer */
DATAFIFO_CMD_WRITE_DONE, /**< When the writer buffer is written, the writer should call this function */
DATAFIFO_CMD_SET_DATA_RELEASE_CALLBACK, /**< When bDataReleaseByWriter is K_TRUE, the writer should call this to register release callback */
DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_AVAIL_WRITE_LEN, /**< Get available write length */
DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_AVAIL_READ_LEN /**< Get available read length */
} k_datafifo_cmd_e;
[Members]
Member Name |
Description |
|---|---|
DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_PHY_ADDR |
Returns the physical address of the DATAFIFO, k_u64 type |
DATAFIFO_CMD_READ_DONE |
After the read end uses the data, it needs to call this to update the head and tail pointers of the read end |
DATAFIFO_CMD_WRITE_DONE |
After the write end finishes writing data, it needs to call this to update the write end’s write pointer. No return value, parameter can be NULL |
DATAFIFO_CMD_SET_DATA_RELEASE_CALLBACK |
Data release callback function |
DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_AVAIL_WRITE_LEN |
Returns the number of data items that can be written, k_u32 type. Note: Since one data item is reserved for buffer management, the actual length available for buffering data is one data item length (u32CacheLineSize) less than the configured DATAFIFO length (u32EntriesNum * u32CacheLineSize) |
DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_AVAIL_READ_LEN |
Returns the number of data items that can be read, k_u32 type |
[Notes]
None
[Related Data Types and Interfaces]
None
4. Error Codes#
4.1 IPCMSG#
Table 41
Error Code |
Macro Definition |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0x1901 |
K_IPCMSG_EINVAL |
Invalid configuration parameter |
0x1902 |
K_IPCMSG_ETIMEOUT |
Timeout error |
0x1903 |
K_IPCMSG_ENOOP |
Driver open failure |
0x1904 |
K_IPCMSG_EINTER |
Internal error |
0x1905 |
K_IPCMSG_ENULL_PTR |
Null pointer error |
0x00000000 |
K_SUCCESS |
Success |
0xFFFFFFFF |
K_FAILURE |
Failure |
0x1901 |
K_IPCMSG_EINVAL |
Invalid configuration parameter |
0x1902 |
K_IPCMSG_ETIMEOUT |
Timeout error |
4.2 DATAFIFO#
Table 42
Error Code |
Macro Definition |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0x1A01 |
K_DATAFIFO_ERR_EINVAL_PARAMETER |
Invalid configuration parameter |
0x1A02 |
K_DATAFIFO_ERR_NULL_PTR |
Null pointer error |
0x1A03 |
K_DATAFIFO_ERR_NOMEM |
Memory allocation failure |
0x1A04 |
K_DATAFIFO_ERR_DEV_OPT |
Device operation failure |
0x1A05 |
K_DATAFIFO_ERR_NOT_PERM |
Operation not allowed |
0x1A06 |
K_DATAFIFO_ERR_NO_DATA |
No data available to read |
0x1A07 |
K_DATAFIFO_ERR_NO_SPACE |
No space available to write |
0x1A08 |
K_DATAFIFO_ERR_READ |
Read error |
0x1A09 |
K_DATAFIFO_ERR_WRITE |
Write error |
0x00000000 |
K_SUCCESS |
Success |
0xFFFFFFFF |
K_FAILURE |
Failure |
5. Debug Information#
5.1 ipcm#
[Debug Information]
msh /bin>cat /proc/ipcm
*---REMOTE NODE: ID=0, STATE: READY
|-RECV BUFFER, PHYS<0x0000000000180000, 0x00079000>
|-SEND BUFFER, PHYS<0x0000000000100000, 0x00080000>
|-Port | State | Send Count | Recv Count | Max Send Len | Max Recv Len
1 Connected 15 15 320 608
*---LOCAL NODE: ID=1, STATE: ALIVE
[Debug Information Analysis]
Records the current usage of the ipcm module.
[Parameter Description]
Parameter |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
REMOTE NODE |
ID |
ID number of the remote processor |
STATE |
State of the remote processor |
|
RECV BUFFER |
Physical address range of the receive buffer |
|
SEND BUFFER |
Physical address range of the send buffer |
|
Port |
Port number |
|
State |
Port connection state |
|
Send Count |
Number of sends |
|
Recv Count |
Number of receives |
|
Max Send len |
Maximum length of data sent |
|
Max Recv len |
Maximum length of data received |