K230 Boot Optimization Guide#
K230 Boot Sequence#
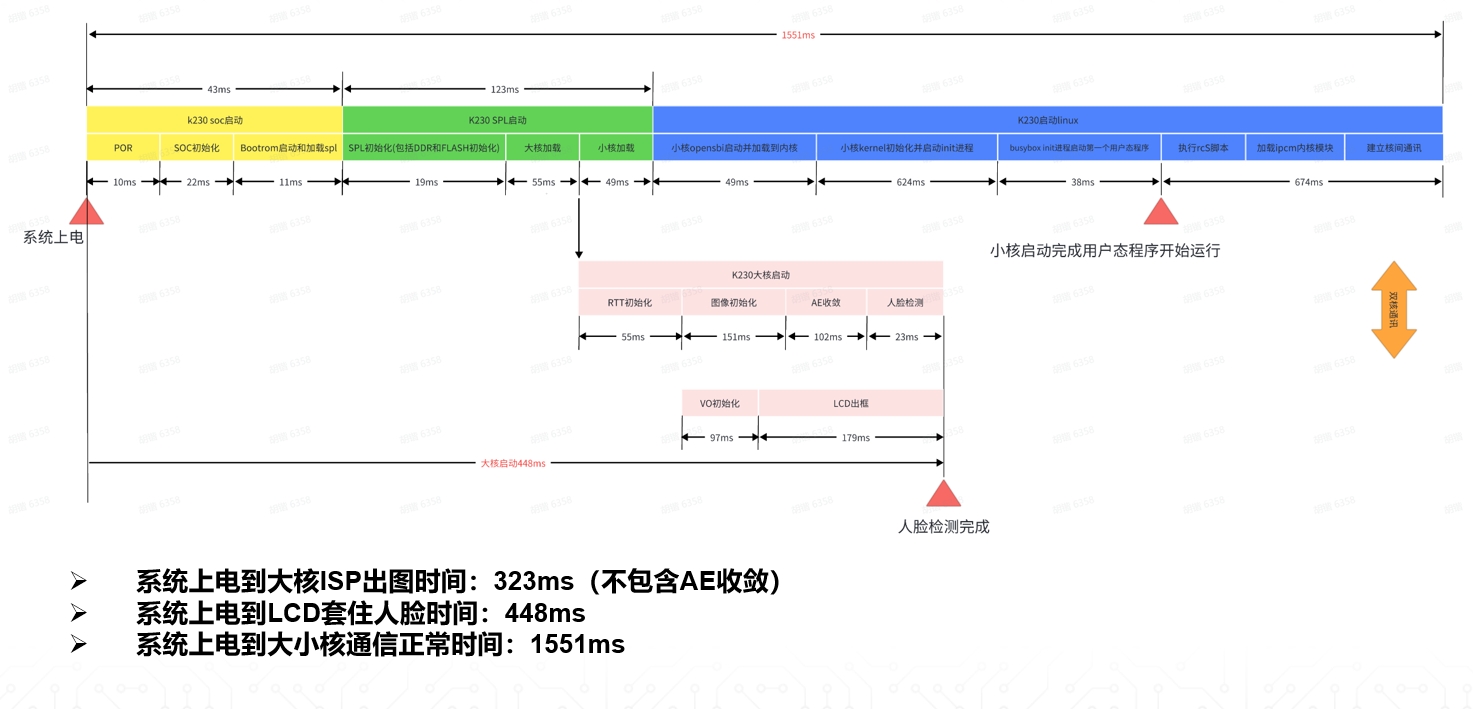
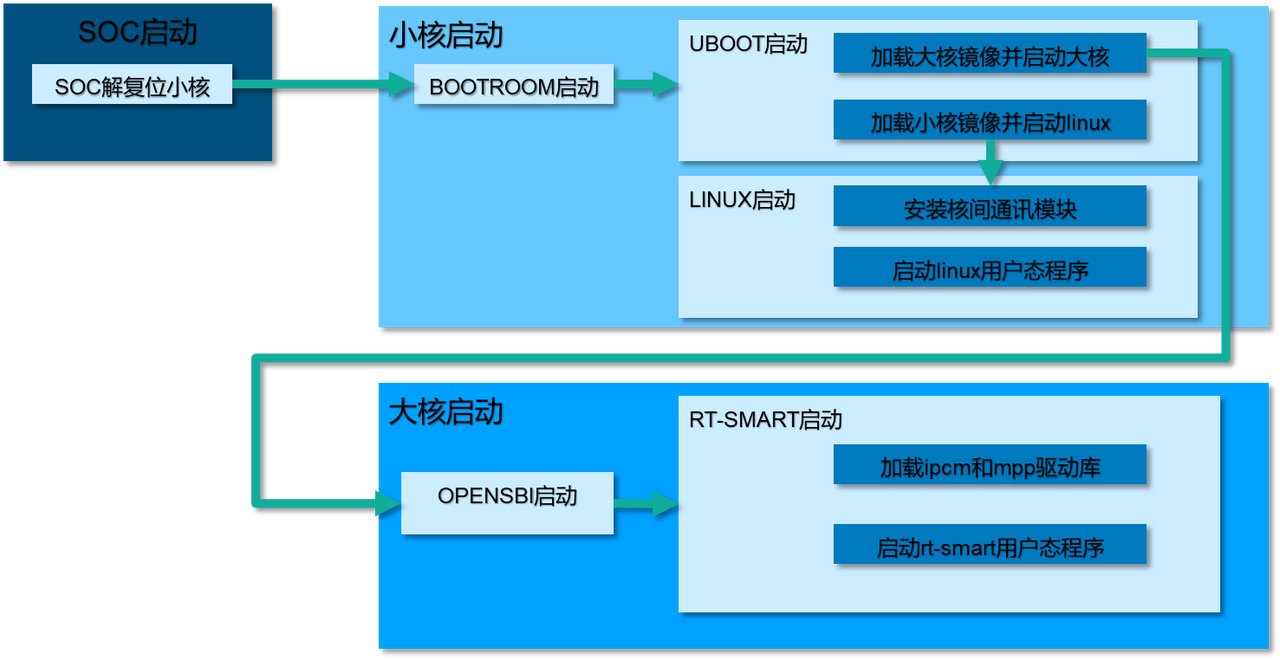
The overall boot process of K230 is shown in the following diagram:
Boot Time Measurement#
Software Measurement#
The CPU core of K230 is RISCV. Users can use the following code in any software on the large or small core to get the current time.
uint64_t perf_get_smodecycles(void)
{
uint64_t cnt;
__asm__ __volatile__(
"rdcycle %0" : "=r"(cnt)
);
return cnt;
}
The obtained value is the number of clock cycles the CPU has run. Dividing it by the CPU frequency gives the current running time. The default clock frequency of the large core in k230_sdk is 1.6GHz, and the clock frequency of the small core is 800MHz.
Hardware Measurement#
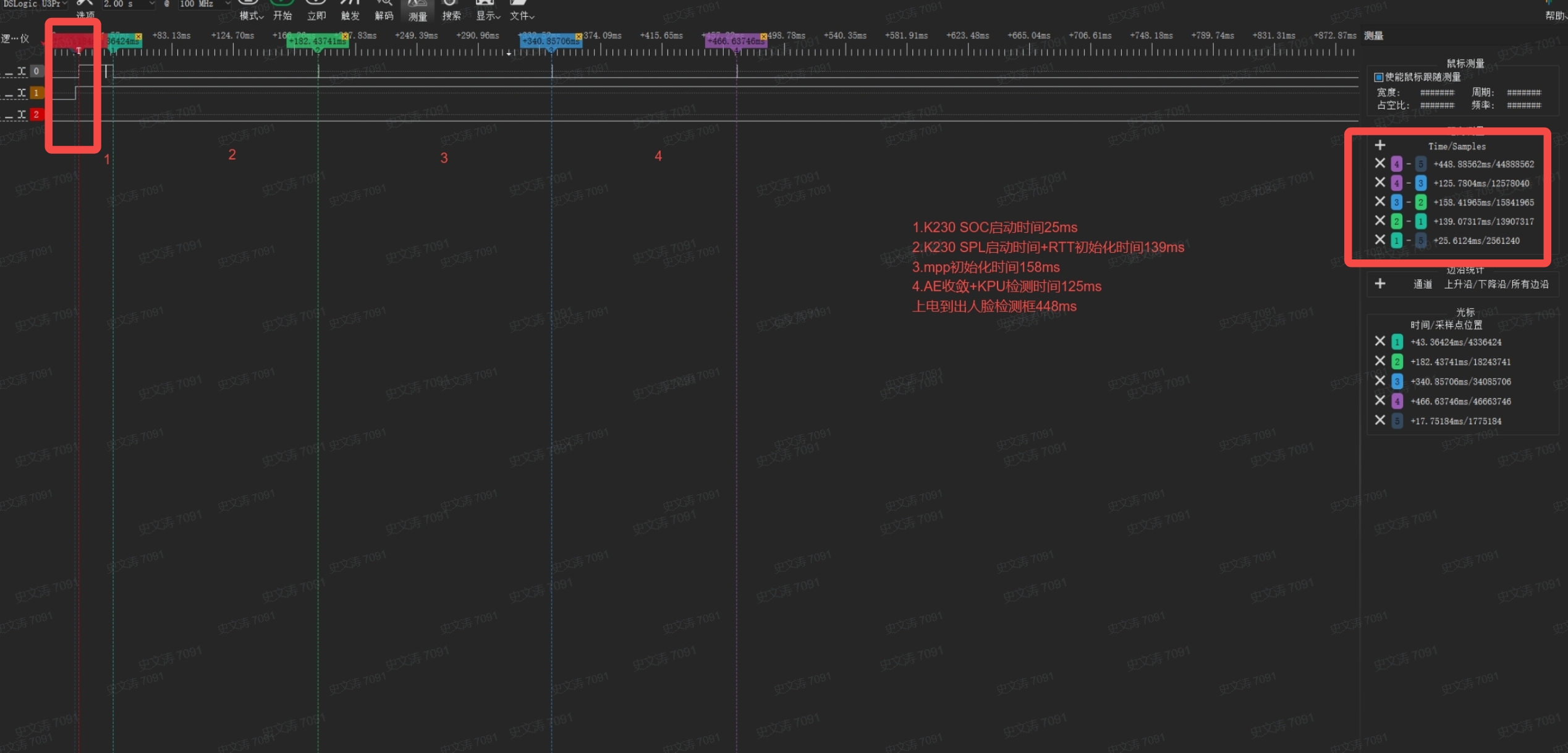
Add GPIO edge changes at the points that need to be measured. More accurate time can be obtained through a logic analyzer or oscilloscope.
You can detect the power-on signal of the development board through pin 14 of J1 on the K230_EVB_LPDDR3_UNSIP board (you need to short-circuit pins 15 and 16 with a jumper cap).
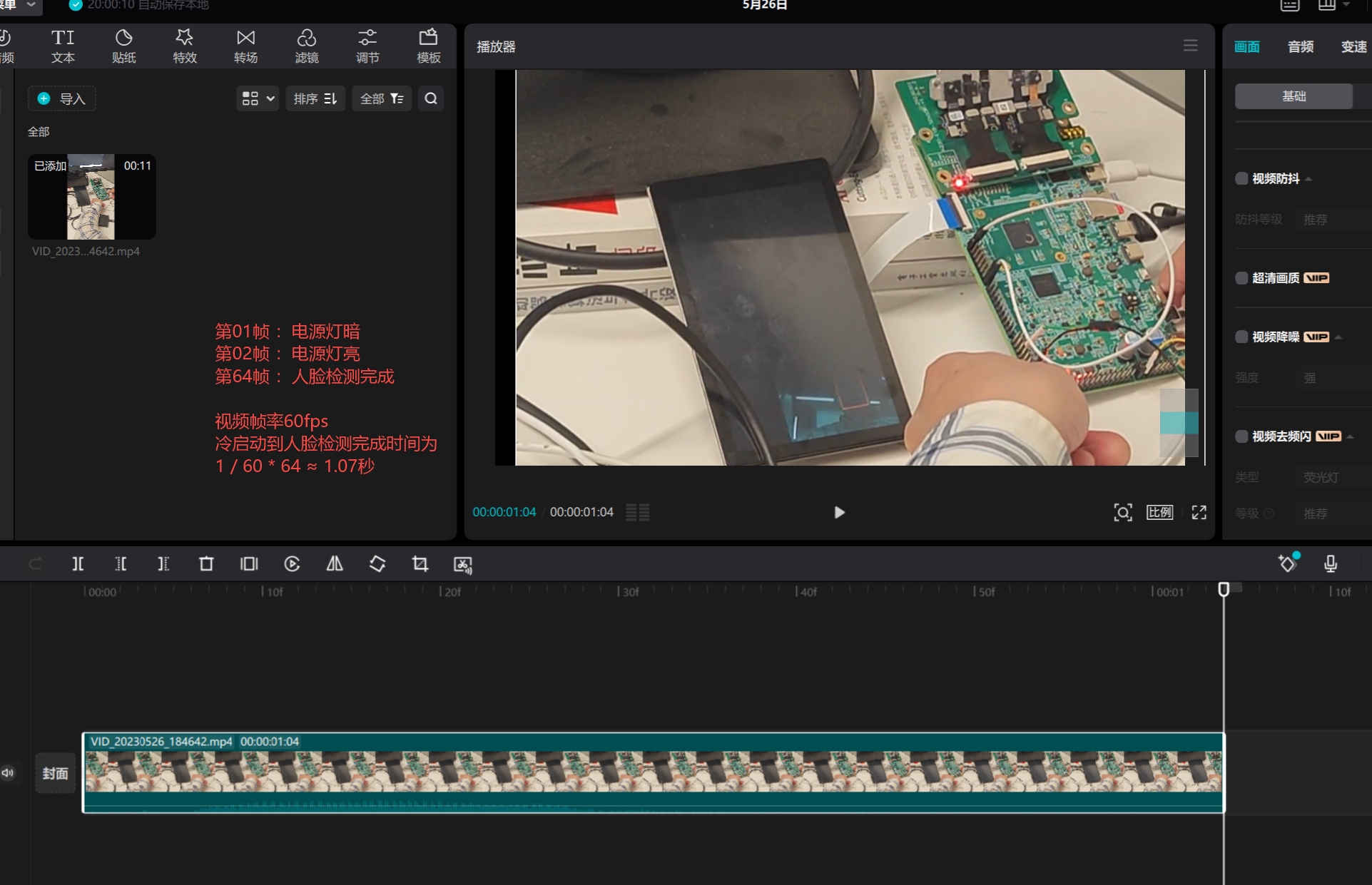
External Observation#
Record the entire system boot process via video. The onboard power light turning on represents the system powering up, and the VO displaying the VI image indicates that the video pipeline is established and can be displayed. A frame appearing around a face indicates that face recognition is completed.
System Trimming#
As seen from the diagram in the previous section, the first step after bootrom starts is to load the large and small core images. Therefore, the first step in optimizing boot time is to trim the large and small core images.
Small Core Trimming#
Linux Image Trimming#
Please refer to the “Linux Module Deletion” section in the document K230_Memory_Optimization_Guide.md.
Rootfs Trimming#
Delete programs or libraries in rootfs that will not be used. For the door lock POC project, this mainly includes the following content. The trimming process refers to the file k230_sdk/board/k230_evb_doorlock/gen_image_script/gen_doorlock_image.sh.
rm -rf usr/bin/fio;
rm -rf usr/bin/lvgl_demo_widgets;
rm -rf usr/bin/ssh*
rm -rf usr/bin/sftp
rm -rf usr/bin/lat*
rm -rf usr/bin/hostapd_cli
rm -rf usr/bin/*test*
rm -rf usr/bin/k230_timer_demo
rm -rf usr/bin/gpio_keys_demo
rm -rf lib/modules/5.10.4+/kernel/drivers/gpu/
rm -rf lib/tuning-server;
rm -rf usr/bin/stress-ng bin/bash usr/sbin/sshd usr/bin/trace-cmd usr/bin/lvgl_demo_widgets;
File System Selection#
The current file systems supported by nor flash are ubifs and jffs2. The door lock POC uses the ubifs image by default. They are both compressed file systems, and the read/write performance of ubifs is stronger than jffs2. Note that when using the ubifs file system, the small core needs to input the halt command before powering off, otherwise, it may damage the file system.
Large Core Trimming#
Large Core Application Trimming#
The strip command will remove symbol information and debugging information from applications and libraries, greatly reducing space occupation. When compiling the door lock POC, the large core application is trimmed in k230_sdk/board/k230_evb_doorlock/gen_image_script/gen_doorlock_image.sh.
/opt/toolchain/riscv64-linux-musleabi_for_x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/bin/riscv64-unknown-linux-musl-strip fastboot_app.elf;
Trimming Effects#
The door lock POC project uses trimmed images by default. The sizes of each image are as follows:
Small core rootfs.ubifs 11M
Small core system compressed image linux_system.bin (opensbi + image + dtb) 3.8M
Large core system compressed image rtt_system.bin (opensbi + rtthread.bin) 1.2M
Large core application fastboot_app.elf 11M
Large core AI models mbface.kmodel + retinaface.kmodel 1.9M
Uboot Boot Optimization#
k230_sdk integrates quick boot configuration for uboot code. Uboot itself runs in two stages: SPL + UBOOT. When quick boot is enabled, SPL will load and run the subsequent large and small core images. When quick boot is not enabled, SPL will load and run the latter half of the UBOOT code. Code location: little/uboot/board/canaan/common/k230_spl.c.
int spl_board_init_f(void)
{
int ret = 0;
device_disable();
g_bootmod = sysctl_boot_get_boot_mode();
ddr_init_training();
memset(__bss_start, 0, (ulong)&__bss_end - (ulong)__bss_start);
if(quick_boot()){//default quick boot
//record_boot_time_info("ls");
ret += k230_img_load_boot_sys(BOOT_SYS_AUTO);
}
ret = k230_img_load_boot_sys(BOOT_SYS_UBOOT);
if(ret )
printf("uboot boot failed\n");
return ret;
}
The return result of quick_boot is affected by the uboot environment variable quick_boot. Users can manually configure it under uboot through the setenv command, or configure quick_boot in k230_sdk through make menuconfig-->board configuration.
Linux Boot Optimization#
Remove Kernel Boot Print#
In the default environment variable configuration of uboot, set fw_devlink to off in the bootargs during flash boot. The code file location is src/little/uboot/board/canaan/common/k230_img.c. The console will no longer print boot logs when Linux starts. After entering the Linux command line, you can view the kernel boot logs through dmesg.
char *board_fdt_chosen_bootargs(void){
char *bootargs = env_get("bootargs");
if(NULL == bootargs) {
if(g_bootmod == SYSCTL_BOOT_SDIO0)
bootargs = "root=/dev/mmcblk0p3 loglevel=8 rw rootdelay=4 rootfstype=ext4 console=ttyS0,115200 crashkernel=256M-:128M earlycon=sbi";
else if(g_bootmod == SYSCTL_BOOT_SDIO1)
bootargs = "root=/dev/mmcblk1p3 loglevel=8 rw rootdelay=4 rootfstype=ext4 console=ttyS0,115200 crashkernel=256M-:128M earlycon=sbi";
else if(g_bootmod == SYSCTL_BOOT_NORFLASH)
//bootargs = "root=/dev/mtdblock9 rw rootwait rootfstype=jffs2 console=ttyS0,115200 earlycon=sbi";
//bootargs = "ubi.mtd=9 rootfstype=ubifs rw root=ubi0_0 console=ttyS0,115200 earlycon=sbi";
bootargs = "ubi.mtd=9 rootfstype=ubifs rw root=ubi0_0 console=ttyS0,115200 earlycon=sbi fw_devlink=off quiet";
}
//printf("%s\n",bootargs);
return bootargs;
Compile Time-Consuming Drivers as Modules#
The door lock POC needs to use USB drivers to connect to the network and MMC drivers to import facial data. These two drivers’ probes are time-consuming and will trigger the probe process of peripheral drivers. Therefore, these drivers need to be compiled as modules. They will be automatically loaded using the modprobe mechanism after the kernel starts. Configurations can be referred to in k230_sdk/src/little/linux/arch/riscv/configs/k230_evb_doorlock_defconfig.
CONFIG_MMC=m
# CONFIG_MMC_TEST is not set
CONFIG_MMC_SDHCI=m
CONFIG_MMC_SDHCI_PLTFM=m
CONFIG_MMC_SDHCI_OF_KENDRYTE=m
CONFIG_USB=y
CONFIG_USB_ANNOUNCE_NEW_DEVICES=y
CONFIG_USB_STORAGE=y
CONFIG_USB_DWC2=m
CONFIG_USB_TEST=m
CONFIG_USB_GADGET=m
CONFIG_USB_SNP_UDC_PLAT=m
CONFIG_USB_CONFIGFS=m
CONFIG_USB_CONFIGFS_MASS_STORAGE=y
CONFIG_USB_CONFIGFS_F_LB_SS=y
CONFIG_USB_CONFIGFS_F_UVC=y
Application Startup Optimization#
Advance the running time of the application. Modify the /etc/inittab file in the root file system to make the first process it runs the program we need to start first. For example, in the k230_sdk/board/k230_evb_doorlock/inittab file, the first process the system starts is sysinit:nice -n -20 /app/door_lock/ui/ui &. This inittab file will replace the original /etc/inittab file in rootfs when compiling the door lock image. The ui program is the small core application program of the door lock POC.
Large Core Boot Optimization#
RT-Smart Boot#
Modify the rt-smart kernel source code to run an init.sh script before the shell thread is established. Define the large core program to run in the script. Code location: big/rt-smart/kernel/rt-thread/components/finsh/shell.c.
if(shell_thread_first_run) {
shell_thread_first_run = 0;
msh_exec("/bin/init.sh", 13);
continue;
}
Application Optimization#
Taking the door lock POC as an example: k230_sdk/src/reference/business_poc/doorlock/big/
The application can initialize various devices through multi-threaded parallelism. For example, inter-core communication and VO initialization can be performed separately in different threads.
pthread_create(&ipc_message_handle, NULL, ipc_msg_server, NULL);
pthread_create(&exit_thread_handle, NULL, exit_app, NULL);
pthread_create(&vo_thread_handle, NULL, sample_vo_thread, NULL);
Other Optimizations#
K230 has a built-in hardware decompression unit. The SDK compiled flash image is a compressed image. Uboot will use the hardware decompression unit to decompress the subsequent large and small core images to improve loading speed.
Optimization Effects#
The boot time statistics of the door lock POC. This statistical data was measured on June 9th, and there may be discrepancies with the current latest SDK version data.